Table of Contents
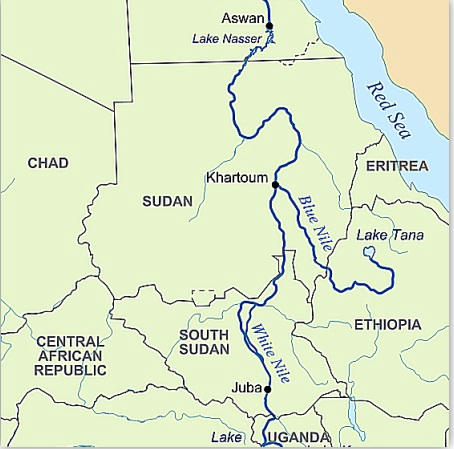
- The river Nile has two major tributaries, the White Nile and Blue Nile.
- Cairo is the city located at the confluence of Both
Choose correct
(A)Only 1
(B) Only 2
(C) Both
(D)None
MCQ 2 – The Report of the Financial Sector Assessment Programme is released by
- WTO
- UNIDO
- IMF
- World bank
- The FSAP follows a three-pronged approach when looking at the country’s financial sector:
- The soundness of a financial system versus its vulnerabilities and risks that increase the likelihood or potential severity of financial sector crises.
- A country’s developmental needs in terms of infrastructure, institutions and markets.
- A country’s compliance with the observance of selected financial sector standards and codes
- The Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) is a joint program of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
- Launched in 1999 in the wake of the Asian financial crisis, the program brings together Bank and Fund expertise to help countries reduce the likelihood and severity of financial sector crises.
- The FSAP provides a comprehensive framework through which assessors and authorities in participating countries can identify financial system vulnerabilities and develop appropriate policy responses.
MCQ 3 –
The United Nations Population Fund has released the State of World Population 2019 report. According to it india grew annually by the rate of
- 2.1 %
- 2.3%
- 1.2%
- 0.5%
- India also recorded an improvement in life expectancy at birth. The life expectancy at birth in 1969 was 47 years and in 2019, it is 69 years.
- India’s population grew at an average annual rate of 1.2 per cent between 2010 and 2019 to 1.36 billion, more than double the annual growth rate of China, according to a report by the United Nations Population Fund.
- India’s population in 2019 stood at 1.36 billion, growing from 942.2 million in 1994 and 541.5 million in 1969. The Indian population grew at average annual rate of 1.2 per cent between 2010 and 2019, the UN sexual and reproductive health agency said, in the State of World Population 2019 report.
- In comparison, China’s population stood at 1.42 billion in 2019, growing from 1.23 billion in 1994 and 803.6 million in 1969. China’s population grew at an average annual rate of 0.5 per cent between 2010 and 2019, the report said.
- Key findings
- According to the report, in India, total fertility rate per woman was 5.6 in 1969, dropping to 3.7 in 1994 and 2.3 in 2019. India also recorded an improvement in life expectancy at birth. The life expectancy at birth in 1969 was 47 years, growing to 60 years in 1994 and 69 years in 2019.
- Giving a snapshot of India’s population composition in 2019, the report said 27 per cent of the country’s population was in the age bracket of 0-14 years and 10-24 years each, while 67 per cent of the country’s population was in the 15-64 age bracket. Six per cent of the country’s population was of the age 65 and above.
Focus on women
- Director of UNFPA Geneva Monica Ferro said the figures were “worrisome” and it was essential to raise the level of consent and access to vital health services for millions of women around the world. “Don’t forget: each one of these numbers is a person,” she said.
- The findings, relating to women aged between 15-49 years, were published for the first time as part of United Nations Population Fund’s (UNFP) State of World Population 2019 report. The report includes, for the first time, data on women’s ability to make decisions over three key areas: sexual intercourse with their partner, contraception use and health care.
- Looking ahead to future challenges, the UN agency highlights the threat to women’s and girls’ reproductive rights posed by emergencies caused by conflict or climate disasters.
- About 35 million women, girls and young people will need life-saving sexual and reproductive health services this year, as well as services to address gender-based violence, in humanitarian settings, it warns. “Every day, more than 500 women and girls including in countries with emergency settings, die during pregnancy and childbirth, due to the absence of skilled birth attendants or emergency obstetric procedures
MCQ 4
- Deepa Malik wins New Zealand PM’s Sir Edmund Hillary Fellowship.
- She is the first Indian woman to win a medal in summer olympic Games
Choose correct
(A) Only 1
(B) Only 2
(C) Both
(D)None
- Paralympian Deepa Malik receives NZ PM’s Sir Edmund Hillary Fellowship
- Malik is a recipient of the Padma Shri, Arjuna Award, and has entered Limca Book of World Records four times.
- As a Sir Edmund Hillary Prime Minister’s Fellow for New Zealand, Deepa will travel to New Zealand and meet with Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern, undertake a series of visits to Paralympic sporting organisations, and engage with Kiwi athletes, students and the media as well as New Zealand’s significant Indian Diaspora community.
- The Fellowship Program has been running since 2008, which aims to strengthen the relationship between India and New Zealand by showcasing the different aspects of the warm friendship between the two countries.
- NITI Aayog CEO Amitabh Kant was the recipient of this prestigious fellowship in 2017.
MCQ 5
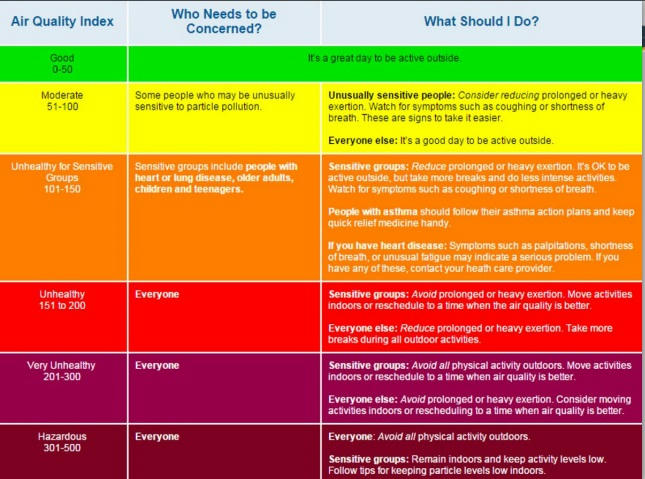
- 1. The Air Quality Index between 0 and 100 is considered “good”.
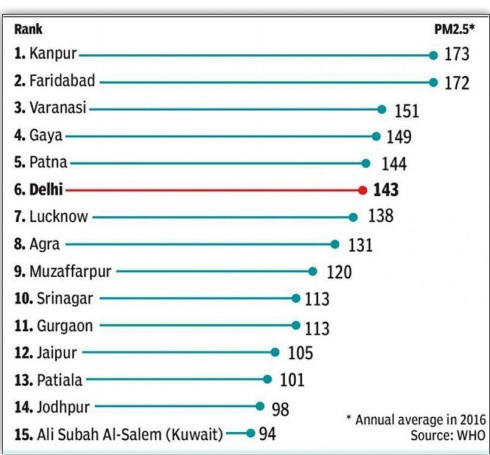
- As per the World Health Organisation, (WHO) list of most polluted cities Varanasi is the most polluted city in the world
Choose correct
(A) Only 1
(B) Only 2
(C) Both
(D)None
- Ambient (outdoor) air pollution in both cities and rural areas was estimated to cause 4.2 million premature deaths worldwide per year in 2016; this mortality is due to exposure to small particulate matter of 2.5 microns or less in diameter (PM2.5), which cause cardiovascular and respiratory disease, and cancers
Key facts
- Air pollution is a major environmental risk to health. By reducing air pollution levels, countries can reduce the burden of disease from stroke, heart disease, lung cancer, and both chronic and acute respiratory diseases, including asthma.
- The lower the levels of air pollution, the better the cardiovascular and respiratory health of the population will be, both long- and short-term.
- The WHO Air Quality Guidelines: Global Update 2005 provide an assessment of health effects of air pollution and thresholds for healthharmful pollution levels.
- In 2016, 91% of the world population was living in places where the WHO air quality guidelines levels were not met.
- Ambient (outdoor air pollution) in both cities and rural areas was estimated to cause4.2 million premature deaths worldwide in 2016.
- Some 91% of those premature deaths occurred in low- and middle-income countries, and the greatest number in the WHO South-East Asia and Western Pacific regions.
- Policies and investments supporting cleaner transport, energy-efficient homes, power generation, industry and better municipal waste management would reduce key sources of outdoor air pollution.
- In addition to outdoor air pollution, indoor smoke is a serious health risk for some 3 billion people who cook and heat their homes with biomass, kerosene fuels and coal.
- The 2005 WHO Air quality guidelines offer global guidance on thresholds and limits for key air pollutants that pose health risks. The Guidelines indicate that by reducing particulate matter (PM10) pollution from 70 to 20 micrograms per cubic metre (μg/m), we can cut air pollution-related deaths by around 15%.
- The Guidelines apply worldwide and are based on expert evaluation of current scientific evidence for:
- Particulate matter (PM)
- Ozone (O3 )
- Nitrogen dioxide(NO2 )
- Sulfur dioxide(SO2 ).
- Please note that the The WHO Air quality guidelines are currently under revision with an expected publication date in 2020.
- The Bill had been drafted in 2006 by the then UPA government. Following that, under the current NDA government, a Group of Ministers (GoM) was constituted under the Union Finance Minister Arun Jaitley. However, the GoM had postponed the legislation, and had introduced the Medical Device Rules and Regulations. The new set of rules was released in 2017, and notified on January 1, 2018.
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) is the national regulatory body for Indian pharmaceuticals and medical devices, and serves parallel function to the European Medicines Agency of the European Union, the PMDA of Japan, the Food and Drug Administration of the United States and the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency of the United Kingdom.
- Within the CDSCO, the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) regulates pharmaceutical and medical devices, under the gamut of Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The DCGI is advised by the Drug Technical Advisory Board (DTAB) and the Drug Consultative Committee (DCC). It is divided into zonal offices which do pre-licensing and post-licensing inspections, post-market surveillance, and recalls when needed
- In India, which is the fourth largest medical devices market in Asia after Japan, China and South Korea, “the need to recognise implants as separate vertical with its own regulatory framework has been ignored”. The fact is that regulation and management is done under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act of 1940.
- Currently, only 23 categories of medical devices are regulated as ‘drugs’ under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 (“D&C Act”). The notified medical devices include disposable hypodermic syringes, disposable hypodermic needles, disposable perfusion sets, in-vitro diagnostic devices for HIV, HBsAg and HCV, cardiac stents, drug eluting stents, catheters, intra ocular lenses, I.V. cannulae, bone cements, heart valves, scalp vein set, orthopaedic implants, internal prosthetic replacements, and ablation devices.
- Blood grouping sera, skin ligatures, sutures and staplers, intra-uterine devices (Cu-T), condoms, tubal rings, surgical dressings, umbilical tapes and blood/ blood component bags are also regulated as ‘Drugs’ under Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940 & Rules, 1945.
- “One peculiar feature of the Indian medical device industry is that it is largely unregulated. The Indian government has regulated only a few types of medical devices. All other types of medical devices are unregulated, meaning there is no government oversight on its manufacture, import, distribution and sale,” says a report on the Indian Medical Device Industry. Though the Medical Device Rules, 2017, which has to come into effect from January 1,2018, has expected to fill the legislative void that is currently present due to the absence of a medical device specific legislation in India, the ICIJ report shows it could not do much.
- As per the report, there was a steady increase in the device related complications in the patients who have undergone implantation surgery. At the same time, Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) data says that “medical device adverse events” rose from 40 in 2014 to 556 in this year.
- At present, Johnson & Johnson faces a case in Supreme Court of India over faulty hip implants that have spoiled the lives of more than 4,000 people. The pharma major marketed devices even after eight years of the product being recalled globally.
- The Coffee Board of India is an organisation managed by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry of the government of India to promote coffee production in India.
- Head Office is in Bangalore.
- The Coffee Board of India was established by an act of Parliament in 1942. Until 1995 the Coffee Board marketed the coffee of many growers from a pooled supply, but after that time coffee marketing became a private-sector activity due to the economic liberalisation in India.
- The Coffee Boards tradition duties included the promotion of the sale and consumption of coffee in India and abroad, conducting coffee research, financial assistance to establish small coffee growers, safeguarding working conditions for laborers, and managing the surplus pool of unsold coffee
- India has replaced Japan as the world’s second-largest steel producing country, while China is the largest producer of crude steel, accounting for more than 51 percent of production, according to World Steel Association.
- The global steel body, in its latest report said, China’s crude steel output jumped 6.6 percent to 928.3 million tonnes in 2018 from 870.9 MT in 2017. China’s share increased from 870.9 MT in 2017.
- China’s share increased from 50.3 percent in 2017 to 51.3 percent in 2018. “India’s crude steel production in 2018 was at 106.5 MT, up 4.9 percent from 101.5 MT in 2017, meaning India has replaced Japan as the world’s second-largest steel producing country. Japan produced 104.3 MT in 2018, down 0.3 percent compared to 2017,” World steel said.
- Global crude steel production reached 1,808.6 MT in 2018 from 1,729.8 MT in 2017, a rise of 4.6 percent, it said.
- Others in the top 10 steel producing countries include the U.S., at the fourth position as the country produced 86.7 MT of crude steel in 2018, South Korea (72.5 MT, fifth place), Russia (71.7 MT, sixth), Germany (42.4 MT, seventh), Turkey (37.3 MT, eight), Brazil (34.7 MT, ninth) and Iran (25 MT, tenth).
- Among other countries, Italy produced 24.5 MT of crude steel in 2018, France (15.4 MT) and Spain (14.3 MT), Ukraine (21.1 MT). The World Steel Association is one of the largest industry associations in the world. Its members represent around 85 percent of the world’s steel production, including over 160 steel producers with nine of the 10 largest steel companies, national and regional steel industry associations, and steel research institutes.
- PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds (PUBG) is an online multiplayer battle royale game developed and published by PUBG Corporation, a subsidiary of South Korean video game company Bluehole.
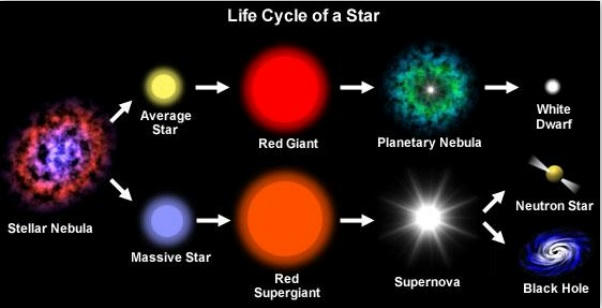
- A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, containing a mass of the order of hundreds of thousands, to billions of times, the mass of the Sun (M2).
- Black holes are a class of astronomical object that have undergone gravitational collapse, leaving behind spheroidal regions of space from which nothing can escape, not even light.
- Observational evidence indicates that nearly all large galaxies contain a supermassive black hole, located at the galaxy’s center.
- In the case of the Milky Way, the supermassive black hole corresponds to the location of Sagittarius A* at the Galactic Core.
- Accretion of interstellar gas onto supermassive black holes is the process responsible for powering quasars and other types of active galactic nuclei.

























 WhatsApp
WhatsApp