Table of Contents
Key Questions
- Discuss provisions, principles & progress of AMRUT scheme.
- a common slum policy does not represent a good use of resources. Discuss.
- Discuss the salient features of Intensified Mission Indradhanush 2.0.
- What are Miyawaki Principles of Natural Forest? Discuss it’s application in Indian context.
- Suggest a Cooperative Model to tackle the problem of stubble burning in Northern India.
- How is Consumer Protection Act 2019 better than the legislation it has replaced?
Discuss basic features, principles & progress of AMRUT scheme.

Background
- Current Urbanization = 34% (UN Report 2018)
- By 2051 => 50%
- Current GDP contribution = 65%
- By 2030 => 70% (McKinsey)
- Access to water = 70% Urban Households
- 49% had access within premises
- Untreated discharge of wastewater = 65%
- Economic Loss = 2.4 trillion (2006) (WB)
3-Level Strategy of Urbanization
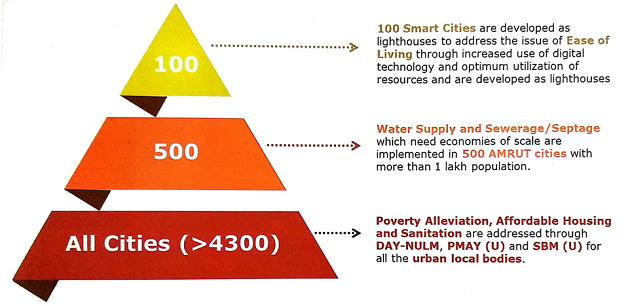
Components of AMRUT
- Focuses on ensuring:
- water supply, sewerage and septage management
- storm water drainage
- urban transport
- availability of green and open spaces
- reform management and support
- capacity building
Coverage of the Scheme
- 476 cities/towns with 1L+ population
- State/UT Capitals not covered in above
- Heritage Cities classified in HRIDAY
- Certain cities on banks of main rivers and from hill States/islands and tourist destinations
Key Principles
1. Cooperative Federalism
- States are empowered to appraise, approve & sanction projects – a departure from JNNURM
2. Framework for Institutional Reforms
- Detailed framework for reforms aimed at improving governance and institutional capacities of ULBs
3. Principles of incrementalism and prioritization
- Step-wise approach towards service level benchmarking by the ULBs for water supply and improving sanitation
4. Incentivizing over Penalizing
- 10% earmarked for incentivizing reforms achieved (earlier 10% penalty)
5. Multi-tier monitoring of the Mission
Progress So Far
- Key figures:
- 64% urban households have tap water supply
- On track to achieve 62% sewerage coverage by 2020
- Key reforms:
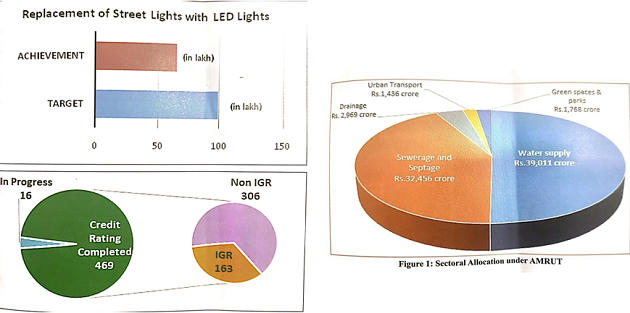
- Online Building Permission System
- Replacement of street lights with LED lights (65 Lakh)
- Credit Rating (36 cities have A and higher rating)
- Municipal Bonds (Ahmedabad, Amravati, Bhopal, Hyderabad, Pune, Surat & Vizag)
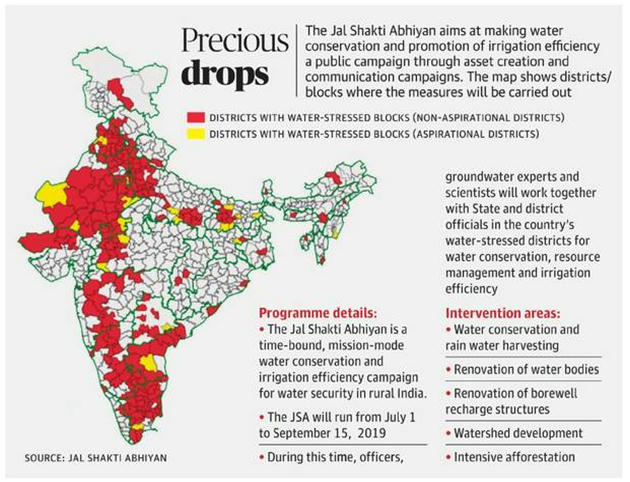
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan – Urban (July 2019) – for water conservation
Jal Shakti Abhiyan
- Aims to ramp up following in 255 water-stressed districts:
- Rainwater harvesting
- Reuse of treated wastewater
- Rejuvenation of water bodies
- Plantation
- Though water is a State issue, the campaign will be coordinated by 255 central IAS officers of Joint or Additional Secretary-rank.
- The campaign follows the model of last year’s Gram Swaraj Abhiyan, where central officials monitored the implementation of seven flagship development schemes in 117 Aspirational districts across the country.
- The campaign ran from July 1 to September 15 in States receiving rainfall during the SW monsoon, while States receiving rainfall in the retreating or NE monsoon will be covered from October 1 to November 30.

Way Forward
- AMRUT envisages to cover > 60% of urban population living in 500 cities with universal coverage of water supply and ~60% sewerage & septage services.
- However, more than 3500 smaller cities/towns out of 4378 statutory towns are present are not covered under any central scheme for water supply & fecal sludge management.
MCQ #1
With reference to the new Union Territories of Ladakh and Jammu & Kashmir, consider the following statements:
- Both the UTs are geographically divided by Ladakh range.
- UT of Ladakh consists of three districts of Leh, Dras & Kargil.
- Select the answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
A common slum policy does not represent a good use of resources. Discuss.

Background
- Slums are self sustaining micro-cities within larger cities
- They are further classified in terms of their social, economic & legal status
- We will discuss some facts & misconceptions which call for a multi-pronged approach to manage a heterogeneous & complex ecosystem called Slums
Fact 1: Official lists under-identify slums and under-count slum populations
- Official records:
- Census 2001 first included slums but only in select cities
- Census 2011 looked at slums in all urban centers
- NSSO 2008 using their definition estimated 44 mn
- Census 2011 using another method estimated 65 mn
- UN Habitat 2014 using another estimated 104 mn
Fact 1: Official lists under-identify slums and under-count slum populations
- With satellite images, researchers identified blue polygons settlements – one type of missed out settlements
- These often have living conditions that are worse than in officially recorded slums.
- Settlement covered by blue tarpaulins (7’ x 7’) tent shared by families of 3 to 5 individuals

Fact 2: Slums have a variety of living conditions that fall along a continuum
- UN Habitat employs 5 criteria to identify slums, each related to a living condition that households usually lack:
- Durable housing of a permanent nature
- Sufficient living space
- Easy access to safe water
- Access to adequate sanitation
- Security of tenure
Fact 2: Slums have a variety of living conditions that fall along a continuum
Fact 2: Slums have a variety of living conditions that fall along a continuum
- Knowing where along the continuum a slum is located helps make public expenditures more relevant and effective.
- Therefore, implementing a common slum policy does not represent a good use of resources.
Fact 3: Traditional survey methods are inadequate. Use satellite imagery.
- Satellite image analysis helps generate slum maps and sort slums into types.
- Coarser-grained images useful for initial slum identification are available for free while finer-grained are not very expensive.
- It is more accurate and less prone to human errors of omission and commission.
Misconception about Slums
- Slums are temporary halting points that work as conveyor belts leading rural migrants into the urban middle class.
- Based on studies in 3 cities:
- On an average, slum dwellers have lived in their current homes for 21 years.
- The majority (66%) have lived in the same home for three or more generations.
- Intergenerational advances in occupational status are minimal. Some in next generation have experienced upward mobility (27%).
Summary
- Overall a situation of stasis – stuck in placidness – is characteristic of slums, whether examined at household or at neighborhood level.
- Satellite images over a 15 year period show that few neighborhoods develop from slum to non-slum areas in terms of physical characteristics.
- Nearly all slum residents, even in the best-off slums, find employment in the informal sector. Less than 5% have jobs that come with security, healthcare & retirement benefits.
MCQ #2
With reference to heart chambers in animals, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Tuna, a fish, has a two-chambered heart.
- Crocodile, a reptile, has a three-chambered heart.
Select the answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Discuss the salient features of Intensified Mission Indradhanush 2.0.

Timeline
- 1978: Expanded Programme of Immunization
- 1985: Universal Immunization Programme
- 2014: Mission Indradhanush
- 2017: Intensified Mission Indradhanush
- 2019: Intensified Mission Indradhanush 2.0
- Will run from Dec 2019 to Mar 2020
Performance
- Between 2009-2013 immunization coverage has increased from 61% to 65%, indicating only 1% increase in coverage every year.
- To accelerate the process of immunization by covering 5% and more children every year, Indradhanush mission was adopted to achieve target of full coverage by 2020.
Factors limiting coverage
- Rapid urbanization
- Presence of a large migrating population
- Presence of isolated populations difficult to reach
- Under-informed & unaware populations
What all is covered?
- Universal Immunization Programme provides life-saving vaccines to all children across the country free of cost to protect them against:
- Diphtheria – Pertussis – Tetanus
- Tuberculosis
- Polio
- Hepatitis B, Pneumonia and Meningitis due to Hib
- Measles
- Rubella
- Japanese Encephalitis (JE)
- Rotavirus diarrhea
- *Rubella, JE and Rotavirus vaccine in select states and districts
IMI 2.0
- Aimed at immunizing children under the age of 2 years and pregnant women
- IMI 2.0 has been launched to focus on 272 districts of 27 states and 652 blocks of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar among hard-to-reach and tribal populations.
- It aims to escalate efforts to achieve the goal of attaining 90% national immunization coverage across India.
Process
- Immunization activity will be in 4 rounds
- Enhanced immunization session with flexible timing, mobile session & mobilization by other departments
- Enhanced focus on left outs, dropouts, and resistant families & hard to reach areas
- Focus on urban, underserved population and tribal areas
- IMI to be conducted till March 2020

MCQ #3
Consider the following statements with respect to the Ghats:
- ‘Anaimudi’ the highest peak of Peninsular plateau is located on the Anaimalai hills of the Western Ghats.
- The Eastern and the Western Ghats meet each other at the Cardamom hills.
- The height of the Western Ghats progressively increases from south to north.
- Most of the Peninsular Rivers have their origin in the Western Ghats.
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- All of the above
What are Miyawaki Principles of Natural Forest? Discuss it’s application in Indian context.
About Miyawaki
- It is a technique pioneered by Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, that helps build dense, native forests.

- Inspiration
- He observed the trees which traditionally grew around temples, shrines, and cemeteries in Japan.
- By promoting natural vegetation on land destroyed by natural & man made disasters, he managed to raise mini forests along the coastline of Japan.

Core Principle
- The basic principle is to initiate high density plantation in small piece of land with native tree species.
- The approach is supposed to ensure that plant growth is 10 times faster and the resulting plantation is 30 times denser than usual.
Other Principles
- No defined spacing b/w plants
- Soil enrichment before plantation
- High density planting of herbs, shrubs & tree species up to 10,000 plants per hectare
- Supplementation of site by seed dibbling of native species
- Mulching to suppress weed and avoid evaporation
- Periodical weeding
- Seedlings of all sizes can be planted to give 3-tier look
Application in India
- Yadadri Natural Forest (YNF) Establishment Model in Telangana
- Principles of local practice and local materials used
- Cost arrived at Rs. 2 L / acre or Rs. 5 L / hectare
- Opportunity:
- Every year 10 Ha natural forest can be created in every village with 1 L plants => natural capital of 50 Ha with 5 L plants over a period of 5 years in every village.
- Protection against natural disasters, soil erosion.
- Promotes water conservation.
MCQ #4
What is the meaning of the word Ijarah commonly used in the later Mughal period?
- The royal land which was distributed to the jagirdars.
- A royal tax levied on the Jagirdars to curb their powers.
- An official scale to measure the land for consolidation.
- A revenue model of farming.
Suggest a Cooperative Model to tackle the problem of stubble burning in Northern India.

What are Cooperatives?
- Cooperativesare people-centred enterprises owned, controlled and run by and for their members to realise their common needs and aspirations.

Problem of Stubble Burning
- The basic reason to burn stubble is the small gap of time b/w harvesting of paddy and sowing of wheat.
- Also, the farmers have limited avenues to dispose off the straw, clean the land and prepare seed bed for wheat well in time.
Solutions
- Measures aimed at reducing/shifting paddy cultivation
- Measures aimed at utilizing the stubble
- Manufacturing of paper, cardboard, etc.
- Production of Mushroom where paddy straw is raw material
- Convert to Energy
How to achieve it on Scale?
- A single unit even of largest size cannot be economical because straw is spread throughout the area and transportation to single point will be a constraint
- Cooperative model, on the lines of Dairy, is most viable and prudent option.
- Need for at least two cardboard and paper manufacturing units in every block.
- Cooperative society with membership of local farmers & farm laborers can be formed and affiliated to an apex body
Swedish Technology being experimented – Torrefaction to convert rice stubble into ‘bio-coal’
- Torrefactionis a thermal process to convert biomass into a coal-like material, which has better fuel characteristics than the original biomass.
- It involves heating up straw, grass, saw mill residue and wood biomass to 250 – 350 degrees Celsius.
- This changes the elements of the biomass into ‘coal-like’ pellets. These pellets can be used for combustion along with coal for industrial applications like steel and cement production
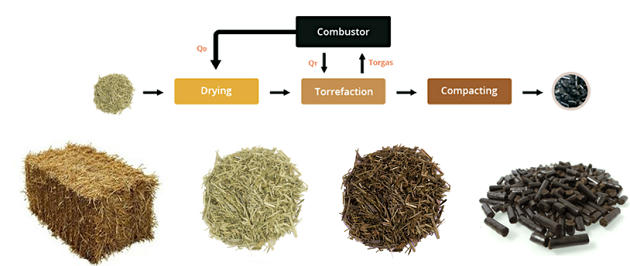
Swedish Technology being experimented – Torrefaction to convert rice stubble into ‘bio-coal’
- It is being brought to India by Bioendev, a Swedish company, which has set up a pilot plant at the National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute in Mohali.
- If scaled up, about 65% of the biomass could be converted to energy.
MCQ #5
Consider the following statements with respect to the formation of new states and alteration of boundaries or names of existing states:
- An amendment is needed for the settlement of a border dispute between the states.
- The Parliament is bound to accept or act upon the views of State legislature.
- The bill for formation or alteration in boundary or the name of a state requires prior recommendation of the president.
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- All of the above
How is Consumer Protection Act 2019 better than the legislation it has replaced?
Limitations of CPA 1986
- CPA 1986 enforces rights of consumers, and provides for redressal of complaints at the district, state and national level.
- It also recognizes offences such as unfair trade practices, which include providing false information regarding the quality or quantity of a good or service, and misleading advertisements.
- Over the years, there have been challenges in the implementation:
- A high number of consumers were unaware of their rights under the Act.
- While the disposal rate of consumer cases was high (about 90%), the time taken for their disposal was long. It took 12 months on an average to resolve a consumer case. => Due to lack of physical & human infra.
- Act does not address consumer contracts between a consumer and manufacturer that contain unfair terms. In this context, the Law Commission of India had recommended that a separate law be enacted.
Highlights of CPA 2019
- Definition of consumer now includes online buyer
- Establishes a regulator – Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) to promote, protect, enforce rights of consumers
- Introduces Product Liability – claim can be made against manufacturer, service provider, and seller
- Introduces Unfair Contracts – as contracts that cause significant change in consumer rights.
- Introduced ADR – mediation cells will be attached to the District, State, and National ommissions
- Increased devolution – pecuniary jurisdiction increased at each of the three levels.
- Defines direct selling, e-commerce and electronic service provider
Download Free PDF – Yojana Magazine
























 WhatsApp
WhatsApp