Table of Contents
What is Economic survey?
- The Economic Survey projects the official version of the state of the economy.
- Generally presented in Parliament a day before the presentation of the annual Budget – it acts as a precursor to the Budget.
- It is prepared and presented by the Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance under the guidance of Chief Economic Advisor
- The Economic Survey document is equally, if not more, important than the Union Budget as it not only lays the premise for key policy decisions that need to be taken to take the economy forward but also assesses the impact of the previous decisions through detailed statistical data
- It discusses the outlook, prospects and challenges of the economy while recommending reform measures that are essential to propel the economy.
CEA – Krishnamurthy Subramanian (Dec 2018 –)

- After a joint address by President Ram Nath Kovind to both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman tabled the Economic Survey 2019-20 in the Parliament on 31st January 2019 .
- “Make money – there is no weapon sharper than it to sever the pride of your foes.” – Thirukural
Theme of Economic Survey 2019-20
- #WealthCreation
- Lavender cover

Historical outlook
- For more than Three-Fourths of Known Economic History, India has been the Dominant Economic Power Globally.
- For this, India Relied on the Invisible Hand of the Market for Wealth Creation with the Support of the Hand of Trust.
- GDP growth for 2019-20 (FY20) – 0% (Lowest in past 10 years)
- GDP growth prediction for 2020-21 (FY21) – 6.0 -6.5 %

Wealth Creation
- The overarching theme of this Survey is Wealth Creation and the policy choices that enable the same.
- The exponential rise in India’s GDP and GDP per capita post liberalization coincides with wealth generation in the stock market.
- Sectors that were liberalized grew significantly faster than those that remain closed. (Rail vs Road transport)
Path to furthering Wealth Creation
- How to strengthen the hand of ‘trust’?
- By promoting pro-business policies
- Introducing the idea of “trust as a public good that gets enhanced with greater use”
- Provide equal opportunities for new entrants, enable fair competition and ease doing business, (‘Pro-Crony’ to ‘Pro-Business’)
- Eliminate policies that undermine markets through government intervention even where it is not necessary,
- Enable trade for job creation, and
- Efficiently scale up the banking sector to be proportionate to the size of the Indian economy.
‘Assemble in India’ into ‘Make in India’
- India has unprecedented opportunity to chart a China-like, labour-intensive, export trajectory.
- Raise its export market share to about 3.5 % by 2025 and 6 % by 2030.
- To Create 4 crore well-paid jobs by 2025 and 8 crore by 2030. use privatization to foster efficiency.
Trust in Govt. Data
- The Survey provides careful evidence that India’s GDP growth estimates can be trusted.
Entrepreneurship and Wealth Creation at the Grassroots
- Entrepreneurship as a strategy to fuel productivity growth and wealth creation.
- India ranks third in number of new firms created, as per the World Bank.
- New firm creation in India increased dramatically since 2014:

- India has jumped up 79 positions in World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business rankings, improving from 142 in 2014 to 63 in 2019.

Ease of Doing Business
- Turnaround Time of Ships Halves from 4.67 Days in 2010-11 to 2.48 Days in 2018-19
- Time Taken For Customs Clearance, Ground handling and Loading At Sea Ports Should Reduce further
- Scope for Improvement in Time Taken in Enforcing Contracts
- Restaurant vs Gun ownership
Banking Sector
- 2019 – Golden jubilee year of bank nationalization
- Accomplishments of lakhs of Public Sector Banks (PSBs) employees cherished and an objective assessment of PSBs suggested by the Survey.
- Since 1969, India’s Banking sector has not developed proportionately to the growth in the size of the economy.
- A large economy needs an efficient banking sector to support its growth.
- India has only one bank in the global top 100 – same as countries that are a fraction of its size: Finland (about 1/11th), Denmark (1/8th)

PSB vs Non PSB
- The onus of supporting the economy falls on the PSBs accounting for 70 % of the market share in Indian banking
- PSBs are inefficient compared to their peer groups on every performance parameter.
- In 2019, investment for every rupee in PSBs, on average, led to the loss of 23 paise, while in NPBs it led to the gain of 9.6 paise.

Privatization and Wealth Creation
- The realized efficiency gains from privatization bolsters the case for aggressive disinvestment of CPSEs.
- Strategic disinvestment of Government’s shareholding of 53.29 per cent in HPCL led to an increase of around Rs. 33,000 crore in national wealth.

‘Thalinomics’
- A plate of nutritious food for the common man- a Thali- is a basic item that every person encounters every day.
- Therefore, there cannot be a better way to communicate whether or not economic policies make the common man better off that qualifying what he/she pays for a Thali every day.
- The survey presents evidence that a Thali has become more affordable for a common man now.
- Absolute prices of a vegetarian Thali have decreased significantly since 2015-16 across India and the four regions; though the price has increased during 2019-20.
From 2006-07 to 2019-20:
- Affordability of vegetarian Thalis improved 29 %.
- Affordability of non-vegetarian Thalis improved by 18 %.

Agriculture Sector
- The survey emphasized on
- mechanization of agriculture,
- livestock and fisheries sector,
- food processing,
- financial inclusion,
- agricultural credit and crop insurance,
- micro irrigation and buffer stock management
- GVA at Basic Prices for 2019-20 from ‘Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing’ sector is estimated to grow by 2.8 %.

Agriculture Mechanization to Transform Indian Farming Into Commercial Farming,
- 9 Per Cent Growth Registered in Livestock Sector During Last Five Years
- 7 Per Cent Average Annual Growth Rate Registered in Fisheries Sector
- 06 Per Cent Average Annual Growth Rate in Food Processing Sector



Inflation
- For FY20
- CPI inflation – 1 %
- WPI inflation – 1.5 %

- During 2019-20 (April-December), the major driver of inflation was food and beverages.
- Among food and beverages, inflation in vegetables and pulses was particularly high due to low base effect and production side disruptions like untimely rain.
Revenue Collection
- Gross GST monthly collections have crossed the mark of Rs. 1 lakh crore for a total of five times during 2019-20 (up to December 2019).
- Centre plus States have been on the path of fiscal consolidation.
Structural reforms undertaken in taxation during the current financial year:
- Change in corporate tax rate.
- Measures to ease the implementation of GST.
- Fiscal deficit of states within the targets set out by the FRBM Act.
Social Infrastructure, Employment and Human Development
- The expenditure on social services (health, education and others) by the Centre and States as a proportion of GDP increased from 6.2 % in 2014-15 to 7.7 % in 2019-20 (BE).
- India’s ranking in Human Development Index improved to 129 in 2018 from 130 in 2017. With 1.34 % average annual HDI growth, India is among the fastest improving countries.
- Gross Enrolment Ratio at secondary, higher secondary and higher education level needs to be improved.
- The share of regular wage/salaried employees has increased by 5 percentage points from 18 % in 2011-12 to 23 % in 2017-18.
- A significant jump of around 2.62 crore new jobs with 1.21 crore in rural areas and 1.39 crore in urban areas in this category.
- Total formal employment in the economy increased from 8 % in 2011-12 to 9.98 % in 2017-18.
- Gender disparity in India’s labour market widened due to decline in female labour force participation especially in rural areas
- Around 60 % of productive age (15-59) group engaged in full time domestic duties.
- Access to health services inter-alia through Ayushman Bharat and Mission Indradhanush across the country has improved.
- Mission Indradhanush has vaccinated 3.39 crore children and 87.18 lakh pregnant women of 680 districts across the country.
- About 76.7 % of the households in the rural and about 96 % in the urban areas had houses of pucca structure.
- A 10 Year Rural Sanitation Strategy (2019-2029) launched to focus on sustaining the sanitation behaviour change and increasing access to solid and liquid waste management.
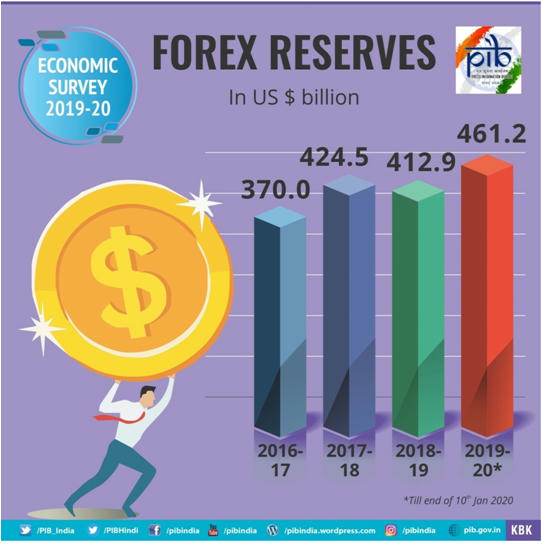
- India’s foreign reserves are comfortably placed at USD 2 billion as on 10th January 2020.
- Further, the external debt levels remained low at 20.1 % of GDP by the end of September 2019.

Economic Survey | Free PDF





















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp