Table of Contents
Direct Benefit Transfer
- Pradhanmantri Garib Kalyan Yojana with an outlay of Rs 1.7 lakh crore which focuses on transfer of funds to the most vulnerable through direct benefit transfer.
- There is a provision for provision of free food grains benefiting about 80 crore of people with additional provision of rice and wheat and pulses free of cost.
- Cash transfer of 6000 rupees to the farmers is proposed.
- Enhancement in pensions , free cylinder delivery for about three months, direct cash benefit transfer to women under Jan Dhan Yojana, provident fund contributions being paid by the government for labour both in the organised and unorganised sector is also part of the scheme.
- Medical insurance scheme to provide insurance cover of 50 lacs to the front line workers fighting corona pandemic premium being paid by the government is also part of the scheme.
- Already an amount of Rs 53248 cr is transferred under the scheme to benefit about 42 crore beneficiaries.
- The pandemic is not behind us. We may still have to keep our powder dry to use it at a later date.
- Direct benefit transfer should be preferred to other modes and schemes to reach the vulnerable sections of population.
- MGNREAS funds can also be transferred as an income support measure to the vulnerable groups who are seeking employment.
- The labour force will also be available all through the year meeting one of the major grievances of the farmers.
- Farmers face severe labour shortage during peak periods of sowing and harvesting.
- Subsidy administration and disbursement leads to building up of vested interests and certain levels of inefficiencies in administering them.
- Direct benefit transfer would help the targeted groups by eliminating these inefficiencies and vested interests and properly worked out can be a win-win situation of saving part of the resources and ensuring benefits directly reach the targeted groups.
PM to CMs
- PM Narendra Modi said “green shoots shoots in the economy” are visible now and economic activities need to be increased.
- In a review exercise with CMs, Modi said Covid danger was not over and there was a need to maintain social distancing.
- The PM cited the example of Punjab to impress upon micro-containment and house-to-house surveillance strategy to combat Covid-19 successfully.
- “The more we can stop the spread of coronavirus, the more we can open up the economy,” the PM told the CMs.
- India’s Covid-19 recovery rate was above 50% and the death rate was low at 0.7 deaths per lakh population.
- Modi pointed to the “green shoots in the economy” such as
- Rising power consumption which was earlier falling
- Doubling of fertilizer sale in May compared to last year
- 13% increase in Kharif sowing this year
- Two-wheeler demand and production reaching 70% of pre-lockdown level
- Digital payment in retail reaching prelockdown level
- Increase in toll collection in May and bouncing back of exports in June to last year’s levels after three months of downfall.
Hindi-Chini Bye Bye
- Govt Official: India’s border tensions with China may not have an immediate impact on business and trade relations.
- There is currently no thought of extending the confrontation to the economic realm.
- China had a surplus of about $47 billion in trade with India in the first 11 months of FY20.
- India’s exports to China in the April 2019-February 2020 period amounted to $15.54 billion with the main items being organic chemicals, fish and ores, while imports stood at $62.37 billion.
- Key imports were electronics, organic chemicals and machinery.
- Small retailers have called for a boycott of goods made in China and the promotion of local products instead to reduce this gap.
- The country had already begun drawing up lists of imports that aren’t critical, most of them made in China.
- Import substitution while improving safety compliance and the quality of goods to gain global market share are among the tenets of India’s Atmanirbhar or self-reliance mission.
- The Confederation of All India Traders (CAIT) on Tuesday released a list of more 450 broad categories of goods that would cut the import bill by ₹1 lakh crore or $13 billion by December 2021.
- They include electronics, fastmoving consumer goods (FMCG), consumer durables, toys, furnishing fabrics, textiles, footwear, apparel, kitchen items, luggage, hand bags, cosmetics, gift items, fashion apparel, food and watches.
- Two major economies of the world —China and India — have serious engagement with each other and defence is just one of them.
- The Asia Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA), previously the Bangkok Agreement, is a preferential tariff arrangement that aims at promoting intra-regional trade through the exchange of mutually agreed concessions by member countries. Its current Members are Bangladesh, China, India, Republic of Korea, Lao PDR and Sri Lanka.
- Mongolia has concluded bilateral negotiations on tariff concessions and is to become the seventh member.
- New Delhi has not been keen to continue its engagement with China in the APTA, the only operational trade pact linking India and China.
- China was a key factor behind India’s exit from negotiations on the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) trade agreement last year as it feared further opening up of trade with the country would dramatically increase the trade deficit.
- India recently tightened its foreign direct investment (FDI) policy for countries it shares a land border with to prevent any opportunistic takeovers during the Covid-19 crisis after China increased its stake in Housing Development Finance Corp (HDFC).
- It is also working on a similar framework for foreign portfolio investors.
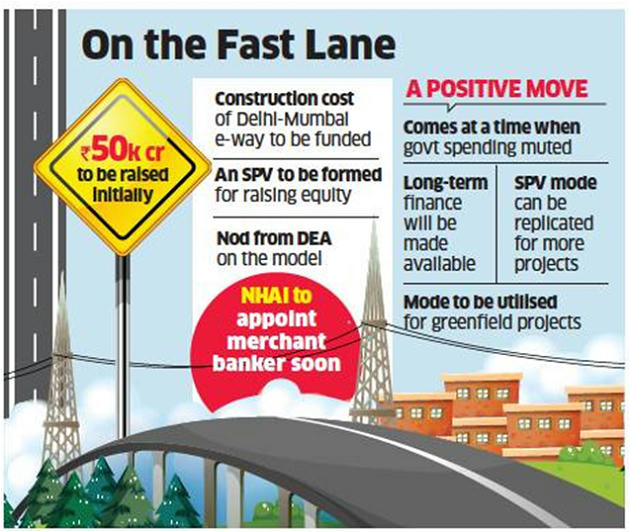
- The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) will go ahead with a plan to raise ₹50,000 crore through a special purpose vehicle (SPV) with the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) for the Delhi-Mumbai expressway project.
NHAI’s ₹50K Cr SPV
- In July last year, the infrastructure funding body entered into an agreement with the national highways building authority to invest in road projects.
- The SPV will allow NIIF to take sovereign funds on board and can co-invest in projects of the NHAI.
- All construction risk and land acquisition costs will be borne by NHAI under the SPV.
- In the first tranche, the construction cost of the 1,320 km long Delhi-Mumbai expressway will be funded.
- NHAI has proposed to use the SPV funding mode for greenfield projects and expressways, according to the official.
Download Free PDF






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp