Table of Contents
TOPICS
1. OVERVIEW – TEXTILE INDUSTRY
2. OVERVIEW – HANDICRAFTS
3. KHADI INDUSTRY
4. TEXTILES & HANDICRAFTS IN NE INDIA

Overview – Textile Industry

TEXTILE INDUSTRY
- The history of textiles in India dates back to the use of mordant dyes and printing blocks around 3000 BC.
- The diversity of fibres found in India, intricate weaving on its state-of-art manual looms and its organic dyes attracted buyers from all over the world for centuries.
- British colonization and its industrial policies destroyed the innovative eco-system and left it technologically impoverished.
- Independent India saw the building up of textile capabilities, diversification of its product base, and its emergence, once again, as an important global player.
MAJOR SECTORS IN TEXTILE INDUSTRY
- Textile industry is divided into following sectors:
- Cotton
- Wool, silk and man-made fibre
- Jute & other vegetable fibre
- Textile products including wearing apparel
- Technical Textiles
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF TEXTILE INDUSTRY
- Contribution of textile industry:
- Size = $150 billion
- 2% to GDP | 14% to industrial production
- Exports = $40 billion | 13% of export earnings
- Employs about 45 million people | 18% of manufacturing
- India is 2nd largest manufacturer & exporter in World, after China
CHALLENGES
- Scale: except spinning, all other sectors suffer from problem of scale
- Skills: paucity of technical manpower
- Raw material: Poor quality and low productivity of cotton
- Innovation/Tech: Lack of R&D
- E.g. synthetic textiles are 50% of global textile market but Indian synthetics are not well developed. Same with technical textiles.
- Institutional Support:
- labor reforms (hindering movement towards higher scale of operations)
- power availability and its quality
- customs clearance and shipment operations from ports
- credit for large scale investments needed for up-gradation of technology
- International Competition: SE Asian countries + China
STEPS TAKEN BY GOVT.
- Offers Rebate of State Levies to textiles exporters
- to offset indirect taxes levied by states such as stamp duty, petroleum tax, electricity duty and mandi tax that were embedded in exports
- Technology Up-gradation Fund Scheme (TUFS) (1999)
- Scheme for Integrated Textile Parks (SITP)
- Integrated Skill Development Scheme
STEPS (CONTD.)
- PM Paridhan Rojgar Protsahan Yojana – incentive to employers by EPF contribution
- Mahatma Bunker Bima Yojana – insurance cover to handloom weavers in natural death
- Bunkar Mitra – Helpline for handholding of Handloom weavers
- Hathkargha Samvardhan Sahayata – govt. bears 90% of the cost of new handlooms
- Deendayal Hastkala Sankul – trade facilitation centre for handicrafts located in Varanasi
- Sustainable and Accelerated Adoption of efficient Textile technologies to Help small Industries (SAATHI) – provide energy efficient power looms
- POWERTEX – aims to boost infrastructure and modernization of the powerloom sector
- Scheme for Capacity Building in Textiles Sector (SCBTS)
- North East Region Textile Promotion scheme
- Integrated Scheme for Development of Silk Industry
MCQ #1
- Moirang Phee is a famous textile of which State?
- Manipur
- Tripura
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
Overview – Handicrafts

HANDICRAFTS
- A simple and workable definition of handicrafts by Development Commissioner (Handicrafts):
- manual labour with minimal or no input from machines;
- a substantial level of skill or expertise;
- a significant element of tradition;
- history of survival in significant scale.
- In India we have > 500 crafts, of which:
- Endangered crafts = 35
- GI Tagged = 92
- Exported > 200
MAJOR HANDICRAFT GROUPS (AS PER NIC)
- Khadi (cloth that is hand-woven from hand-spun yarn)
- Cotton handlooms and silk handlooms
- Hand processing of cotton textile and silk textile
- ‘Zari’ (silver and gold thread work) and embroidery
- Carpets
- Leather manufacture
- Earthenware
- Plating/polishing/engraving of metals
- Jewellery and related articles
- Making of musical instruments
- Miscellaneous products of wood, bamboo, cane and grass
SOCIAL IMPORTANCE OF HANDICRAFTS
- High Employment Intensive sector
- Diversifies income base of farmer-artisan
- High employability of woman
- Socially inclusive – artisans across caste groups
- Decentralized – mostly located in rural areas
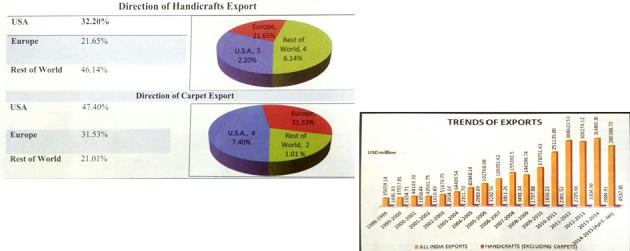
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF HANDICRAFTS
- Handicraft Artisans ~ 70 Lakh (11th FYP) (56% women)
CHALLENGES
- Changing Consumption Poses a Challenge
- Increasing Competition Abroad
- Raw Material Scarcity
- Corruption and Administrative Inefficiency
- Environmental and Social Concerns
OTHER CHALLENGES
- Problems Specific to Crafts Producers
- Limited Information and Capability
- Lack of finance
- Lack of social status
- Problems Specific to Traders and Exporters
- Credit
- Transactions costs
- Design protection
- Government policy
- E-commerce
STEPS TAKEN BY GOVT. : MARKETING
- Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts organizes:
- product specific shows
- Indian Handicrafts & Gifts Fairs (annually)
- Market Development Assistance
- Market Access Initiative
- Indian Handloom Bazaar – e-portal
- Hastkala Sahyog Shivirs (400 in 200 districts in 2017)
- Geographical Indicator Tags e.g. Kangra Paintings, Varanasi brocades & saris, Bastar wooden craft, etc.
MCQ #2
- Raghurajpur village, famous for Pattachitra, is in which state?
- Odisha
- Jharkhand
- West Bengal
- Bihar

KHADI INDUSTRY
- Khādī or Khaddar is a term for hand spun and hand-woven cloth from India, Bangladesh and Pakistan primarily made out of cotton.
- Khadi = Hand spun + Hand woven
- Handloom = Machine spun + Hand woven
- Raw materials may also include silk, or wool, which are all spun into yarn on a spinning wheel called a charkha.
- It is a versatile fabric, cool in summer and warm in winter. In order to improve the look, khādī/khaddar is sometimes starched to give it a stiffer feel.
KHADI MOVEMENT IN INDIA
- In 1918 Mahatma Gandhi started his movement for Khadi as relief programme for the poor masses living in India’s villages.
- It was to be an agent of change for providing livelihood, self-sufficiency and at a moral plane inculcate virtues like patience.
INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK
- Khadi & Village Industries Commission (KVIC), established under KVIC Act, 1956, is engaged in promoting and developing khadi and village industries.
- Main objectives of KVIC include:-
- social objective of providing employment in rural areas;
- economic objective of producing saleable articles; (2017 => 50k Cr)
- wider objective of creating self-reliance and strong community spirit.
- KVI today represent an exquisite, heritage product, which is ‘ethnic’ as well as ethical.
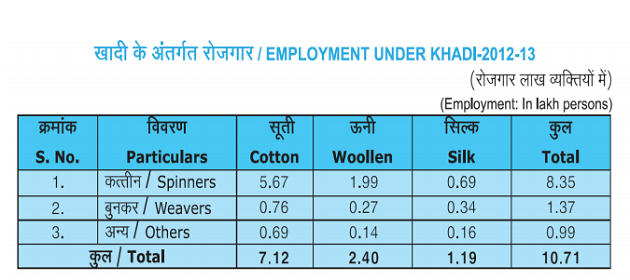
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE : EMPLOYMENT
MARKETING
- Need to change mindset:
- People should buy khadi not as a “national duty” or “act of charity” but because it is fashionable, admired the world over, and intrinsically of high value. Khadi be promoted as fashion product and eco-friendly.
- Shops to be opened in all international airports in India and the possibility of marketing through e-commerce must be explored.
- Huge charkhas have been set up at IGI Airport and Connaught Place
- Need for a khadi mark on the lines of handloom/ silk mark.
- New products / designs will be developed with the help of NID and NIFT.
- Under Product development, design intervention and packaging (PRODIP), incentives for development of new products, designs and better packaging have been introduced.
- Khadi mitra is on the cards – where housewives could sell Khadi with a very nominal capital investment.
MCQ #3
- Screw pine craft is famously practiced in which state?
- Tamil Nadu
- Himachal Pradesh
- Kerala
- Jammu & Kashmir

INTRODUCTION
- NE India has a lot of heterogeneity in terms of culture.
- Textiles and dresses are dominant cultural aspects.
- Development of textiles & handicrafts is an imp tool for regional development of NE India.
WEAVING
- Practiced by most of the tribal groups in NE India
- Some exceptions => Nokteys of Tirap in Arunachal and Khasis of Meghalaya
- Meghalaya is known for establishing tradition of high quality weaving. Arunachal is famous for their beautiful color combinations.
- Exceptional are: Sherdukpen shawls, Apatani jackets and scarves, Mishmi shawls, Naga shawls, etc.
Apatani Weaves

SILK
- Assam is 3rd largest producer of silk in India and is home to various types of silk. Muga is coveted.
- Manipur produces ~100% of Oak tasar silk and is highest producer of mulberry silk in NE India.
- Tripura focuses on production of only Mulberry silk with end to end solutions.
BAMBOO & CANE CRAFT
- Weather conditions are conducive for bamboo.
- Mizos take great pride in their cane and bamboo work.
- Most of Naga tribes are adept at wood & bamboo.
- Assamese life revolves around cane & bamboo goods.
- Jappi, a traditional sun shade, remains the most significant bamboo article.


OTHERS
- Carpets
- Most ancient form of carpet weaving is found in Sikkim
- Arunachal is also famous for it’s carpets
- Wooden & metal products
- Sikkim excels in wood carving while it is a significant hobby of the Wanchos of Tirap in Arunachal
- Rengma tribe is considered to be the best Naga black smith for e.g. beautifully decorated spears





















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp