Table of Contents
TOPICS
- YOGA: AN OVERVIEW
- YOGA & MENTAL HEALTH
- ALTERNATE SYSTEM OF MEDICINE IN INDIA
– EVOLUTIONOF MEDICINE SINCE ANTIQUITY
– HISTORY OF MEDICINE IN INDIA
- AYURVEDA -> SIDDHA -> UNANI
- HOMEOPATHY
- SOWA-RIGPA -> NATUROPATHY
– GOVERNANCE OF INDIAN ASM

YOGA: AN OVERVIEW
- Yoga philosophy is one of the six major orthodox schools of Hinduism
– Others: Samkhya, Nyaya, Vaisheshika, Mimamsa and Vedanta.
- The origins are unclear, but first references can be found in the Upanishads from 1st millenium B.C.E.
- The systematic collection of ideas of the Yoga school of Hinduism is found in the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali.
YOGA VS. SAMKHYA
- Yoga philosophy is closely related to Samkhya, but unlike Samkhya, yoga accepts the concept of God.
– While Samkhya states that knowledge is the only path to moksha, yoga says that it should be combined with systematic practice, or personal experimentation.
- Patanjali outlines the eight limbs, or stages, that one should follow to reach moksha.
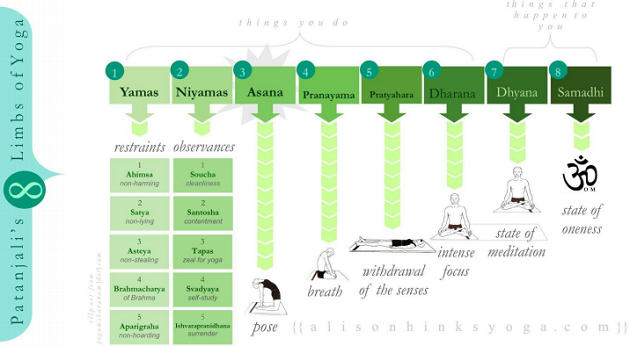
PROMOTION OF YOGA


MCQ #1
- Which of the following is an heterodox school of Indian Philosophy?
- Carvaka
- Ajivika
- Buddhism
- All of the Above

YOGA & MENTAL HEALTH
- Yoga is described as holistic health system
- As per Yoga, diseases are caused by – Stress, Wrong diet, Wrong exercise and Bad habits.
- Yoga brings about positive health by:
– Relaxing the whole body
– Making respiration quiet and deep
– Calming the mind
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
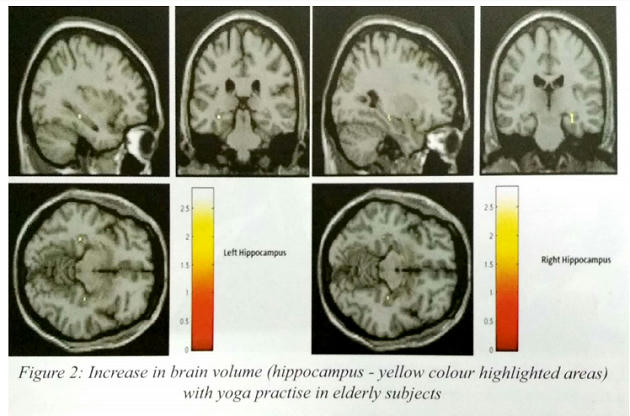
- Research at NIMHANS has shown that yoga has effects on biological parameters like:
– Reducing cortisol levels
- Cortisols are nature’s built-in alarm system. It’s your body’s main stress hormone. It works with certain parts of your brain to control your mood, motivation, and fear.
– Decreasing neuro-inflammation in patients
- Yoga can be used as an add-on therapy or in some instances as sole therapy for psychiatric disorders.

YOGA FOR POSITIVE MENTAL HEALTH
- Ahara (Food) – 50% food + 25% water + 25% air
- Vihara (Relaxation) – asana, meditation, sleep, etc.
- Achara (Conduct) – controlling desires
- Vichara (Thinking) – controlling thoughts
- Vyavahara (Behavior) – right actions
MCQ #2
- ‘Synapse’ is part of which system in Human body?
- Circulatory System
- Respiratory System
- Nervous System
- Reproductive System

EVOLUTION OF MEDICINE SINCE ANTIQUITY
- 3000 to 3500 BC: Early medicine practices in every culture
- Around 200 BC: these practices started influencing each other and 800 AD onwards, a major convergence of these practices
- Mid-15th century: beginning of scientific or modern medicine.
- Mid-19th century: Allopathy distinguished from Homeopathy by C.F.S. Hahnemann
– In Allopathy, disease is treated by the use of remedies which produce effects different from those produced by the disease under treatment
– In Homeopathy, disease can be treated with drugs thought capable of producing the same symptoms in healthy people as the disease itself

HISTORY OF MEDICINE IN INDIA
- The study of history of medicine in India can be divided into 4 phases:
– Ancient Indian medicine;
– Indian medicine in medieval times;
– Indian medicine during the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century;
– Progress after Independence in India (1947 to date)

ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | AYURVEDA
- With the Aryan Invasion of India, the Vedic period of the Indian system of medicine may be said to have begun.
- The Indian system of medicine ‘Ayurveda‘ which literally means knowledge of life, is strictly not a Veda like the four Vedas, but is considered to be an Upaanga of the Atharvaveda.
– This would thus give it divine authority.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | BASICS OF AYURVEDA
- The concept of man in his entirety – physical (including chemical), and biological (including psychological and spiritual) – became the basis for the study of medicine.
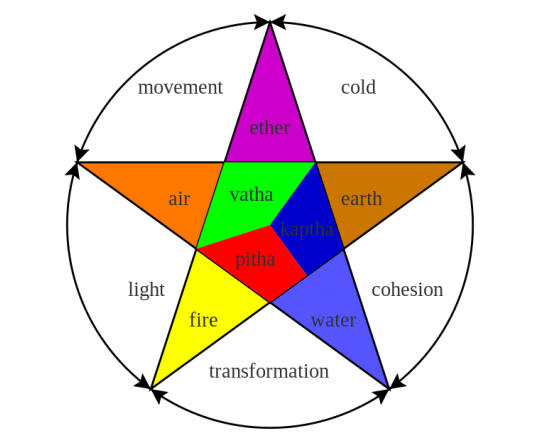
- It believes that all objects in the universe including human body are composed of five basic elements namely, earth, water, fire, air and sky.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | BASICS OF AYURVEDA
- The medicine system was based on the system of ‘TRIDOSHA – KAPHA (phlegm), VATA (wind) and PITTA (bile), existing in a balanced proportion in health.
- A disturbance in this balance resulted in disease with its attendant ailments.
- 3 primary dosha were connected with 3 gunas
– sattva (goodness, constructive, harmonious)
– rajas (passion, active, confused)
– tamas (darkness, destructive, chaotic)
- Food and medicines were classified according to their ‘cooling’ or ‘heating’ effects.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | MEDICATION IN AYURVEDA
- Anatomical knowledge was derived principally from:
– sacrifice of animals
– chance observations of improperly buried bodies
– examinations of patients by physicians
- In the treatment of diseases, observance of a diet regime is a very essential part of treatment.
- A large number of herbal medicines of indigenous origin formed the materials of treatment.
- This was followed by ‘Rasa period’, when minerals were used; thus iron, zinc, copper, lead, gold and mercury were used in therapeutics.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | WORKS OF AYURVEDA
- Two main sets of texts form the foundation of Ayurvedic medicine, the Sushruta Samhita and the Charaka Samhita.
– Sushruta Samhita was written by the famous physician and surgeon Sushruta.
– Charaka lived in mid 2nd century BC and was associated with Taxila University
- AACHARYA VAGBHAT (400 A.D.) combined the topics from Charaka Samhita and Sushruta Samhita to produce a concise prose composition known as ASHTANG SANGRAHA.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | WORKS OF AYURVEDA
- Vagbhat further wrote ASHTANG HRIDAYA which converted Ayurvedic knowledge from prose into verse form, making it easier to memorize.
- Madhava Nidhana (700 A.D.), Shranghdhar Samhita (1300 A.D.), Bhavprakash (1600 A.D.), and Kashyap Samhita are other important works on Ayurveda, published at a later period.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | AYURVEDA GOVERNANCE
- 1953: Central Research Institute for Ayurveda
- 1963: PG Institute of Indian Medicine at BHU
- 1969: Central Council for Research in Indian Medicine & Homeopathy (CCRIM&H)
- 1978: Central Council for Research in Ayurveda & Siddha (CCRAS) – (bifurcated in 2011)
- 2014: full fledged Ministry of AYUSH
MCQ #3
- National Ayurveda Day is celebrated in India on the birth of Lord ____________


ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | SIDDHA
- The name Siddha oushadha (siddha medicine) relates to the earlier esoteric medicinal postulates concerning longevity, even immortality, and the later iatrochemical formulations as conceived and practiced by 18 Siddhas, located in Tamil Nadu.
– The term Siddha means achievements.
– Iatrochemistry seeks to provide chemical solutions to diseases
- It is most prominent in Tamil Nadu but is also popular in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka and Kerala.
- Outside India, it is common in Sri Lanka, Malaysia and Singapore where the Dravidian civilisation had taken roots.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | BASIS OF SIDDHA
- Like Ayurveda, it believes that all objects in the universe including human body are composed of five basic elements namely, earth, water, fire, air and sky.
– The food, which the human body takes and the drugs it uses are all, made of these five elements.
- The proportion of the elements present in the drugs vary and their preponderance or otherwise is responsible for certain actions and therapeutic results.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | BASIS OF SIDDHA
- Siddha practitioners have adopted Ayurvedic concept of Tridosha — Vaadham, Pittham and Kapam.
- The food is considered to be basic building material of human body which gets processed into humours, body tissues and waste products.
- The equilibrium of humours is considered as health and its disturbance or imbalance leads to disease or sickness.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | SIDDHA MEDICINE
- Siddha tradition has incorporated minerals and metals, many of which are very toxic (mercury, sulphur, arsenic, etc.). and vegetable poisons. In this, it is similar to Rasa Shastra of Ayurveda.
- It received patronage of Tamil kings and the chieftains as well as general public.
- Since Independence, the govt. has encouraged the system very considerably.
ANCIENT INDIAN MEDICINE | CURRENT STATUS OF SIDDHA
- Tamil Nadu state runs a 5.5-year course in Siddha medicine (BSMS: Bachelor in Siddha Medicine and Surgery).
- Indian Government also gives its focus on Siddha, by starting up medical colleges and research centers like:
– National Institute of Siddha
– Central Council for Research in Siddha
MCQ #4
- International Day of Yoga coincides with:
- Spring Equinox
- Autumn Equinox
- Summer Solstice
- Winter Solstice

INDIAN MEDICINE IN MEDIEVAL TIMES | UNANI
- Unani is a tradition of Graeco-Arabic medicine based on the teachings of Greek physician Hippocrates, and Roman physician Galen.
- It developed into an elaborate medical system by Arab and Persian physicians, the most famous being the Muslim scholar Hakim Ibn Sina (known as Avicenna in the west).
- He was primarily influenced by Greek and Islamic medicine, and was also influenced by the Indian medical teachings of Sushruta and Charaka.
INDIAN MEDICINE IN MEDIEVAL TIMES | BASIS OF UNANI
- Unani is very close to Ayurveda.
- It is based on the concept of 4 humours:
– Phlegm (Balgham)
– Blood (Dam)
– Yellow bile (Ṣafrā)
– Black bile (Saudā)
- These elements are present in different fluids and their imbalance leads to illness.
INDIAN MEDICINE IN MEDIEVAL TIMES | UNANI IN INDIA
- When Mongols ravaged Persian and Central Asian cities like Shiraz, Tabrez and Galan, scholars and Physicians of Unani Medicine fled to India.
- Delhi Sultans, the Khiljis, the Tughlaq and the Mughal Emperors provided state patronage to the scholars and even enrolled some as state employees and court physicians.
– Akbar’s reign can rightly be regarded as the flourishing period of Unani.
INDIAN MEDICINE IN MEDIEVAL TIMES | UNANI-AYURVEDA INTERACTION
- Many medical works of high standard were compiled during this age which undoubtedly point out the predominant influence of Ayurveda upon Unani system and vice versa.
- It appears from Bhavaprakasha’s study that Ayurveda borrowed and assimilated a significant number of simple drugs like henbane, rhubarb and opium, etc., from Unani medicine.
- Muslim Hakims and Hindu Vaidyas cooperated and worked together; and Unani and Ayurvedic systems were followed simultaneously.
INDIAN MEDICINE IN MEDIEVAL TIMES | BRITISH ERA
- During the British rule, Ayurvedic and Unani Medicine suffered a setback and its development was hampered due to withdrawal of governmental patronage.
- In spite of all these setbacks, however, Ayurvedic medicine, and to some extent Unani medicine, have persisted in India throughout the centuries.
– Unani has found favour in India where popular products like Roghan Baiza Murgh (Egg Oil) and Roghan Badaam Shirin (Almond Oil) are commonly used for hair care.

MCQ #5
- NAMASTE Portal is an initiative by which Ministry?
- Ministry of Tourism
- Ministry of External Affairs
- Ministry of Science & Technology
- None of the above
FROM TRADITIONAL TO MODERN MEDICINE
- Hippocratic tradition continued both in Europe and the middle east without much modification till the 14th and 15th century, when the Black Death (Great Plague) devastated both the Middle East and Europe.
- This led to a major shift in medical thinking. Modern scientific research began to replace early Western traditions based on herbalism, the Greek “four humours” and other such pre-modern notions.
BEGINNING OF MODERN MEDICINE
- The modern era really began with Edward Jenner’s discovery of the smallpox vaccine at the end of the 18th century (inspired by the method of inoculation earlier practiced in Asia).
- Allopathy is defined as that discipline advocating therapy with remedies that produce effects differing from those of the disease treated.
- It is also called ‘modern’, ‘western’, or ‘scientific’ medicine.
BEGINNING OF MODERN MEDICINE IN INDIA
- Western medicine in India really began with the promulgation of the Quarantine Act of 1825, which marked the start of the public health movement in India.
- Around the same time, Homeopathy, which originated in Germany a century ago, came into India.

ORIGINS OF HOMEOPATHY
- It originated in 1796 by Samuel Hahnemann, based on his doctrine of similia similibus curentur (“like cures like”), according to which a substance that causes the symptoms of a disease in healthy people will cure similar symptoms in sick people.

HOMEOPATHY IN INDIA
- Homoeopathy came to India as early as 1810 when a French traveller, Dr. John Martin Honigberger who learnt Homoeopathy from Dr. Samuel Hahnemann visited India and treated patients with Homoeopathy.
- In his second visit in the year 1839, he treated the then ruler of Punjab, Maharaja Ranjit Singh with Dulcamara.
- Maharaja was so happy with results and he encouraged him to continue the Homoeopathic treatment in India.
HOMEOPATHY IN INDIA
- In 1861, a virulent epidemic of malarial fever was raging over lower Bengal and it was at this juncture that the great philanthropist, Babu Rajendra Lall Dutta, a layman, truly laid the foundation of Homoeopathy and started its practice with astounding results.
- He converted the redoubtable allopath and his opponent, Dr. Mahendra Lall Sircar to Homoeopathy.
– Dr. Mahendra Lal Sircar was instrumental in spreading the prestige and fame of homoeopathy far and wide in India.
HOMEOPATHY GOVERNANCE IN INDIA
- 1973: Central Council of Homeopathy
- 1975: Homeopathic Pharmacopoeia Laboratory
- 1975: National Institute of Homeopathy
- 1978: Central Council for Research in Homeopathy
Sowa Rigpa
SOWA-RIGPA: ORIGINS
- “Sowa-Rigpa” (Science of healing) commonly known as Amchi system of medicine is one of the oldest, living and well documented medical tradition of the world.
- It has been popular in Tibet, Magnolia, Bhutan, some parts of China, Nepal, Himalayan regions of India and few parts of former Soviet Union etc.
SOWA-RIGPA IN INDIA
- Some scholars believe that it is originated from India; some says China and others consider it to be originated from Tibet itself.
- Majority of theory and practice of Sowa-Rigpa is similar to “Ayurveda”:
– The first Ayurvedic influence came to Tibet during 3rd century AD but it became popular only after 7th centuries with the approach of Buddhism to Tibet.
– There after this trend of exportation of Indian medical literature, along with Buddhism and other Indian art and sciences were continued till early 19th century.
SOWA-RIGPA: GOVERNANCE
- There is Central Council for Tibetan Medicine in Dharamsala to regulate the practice of Sowa-Rigpa.
- It looks after the registration of practitioners, standard of colleges and other mechanism to regulate SowaRigpa.

NATUROPATHY
- Naturopathy is a drugless non-invasive rational and evidence based system of medicine imparting treatments with natural elements.
- Principle: accumulation of toxins is the root cause of all diseases. Prevention and elimination of toxins is the route to health.
TREATMENT
- Treatment: based on the 5 great elements of nature. There is no role of internal medications in the nature cure system.
– Earth
– Mud Therapy (Mud baths, Mud packs)
– Water
– Hydrotherapeutic methods in the form of Baths, Jets, Packs, Compresses, Immersions
– Air – Breathing exercises, Outdoor walking, Open air baths
– Fire – Sun baths, Diet therapy
– Ether – Fasting therapy
MAJOR THERAPEUTIC MODES
- Fasting Therapy
- Diet Therapy
- Mud Therapy
- Hydro Therapy
- Massage Therapy
- Helio Therapy
- Air Therapy
- Yoga Therapy
MCQ #6
- “India: A Wounded Civilization” was authored by:
- Lord Bentinck
- Lord Wellesley
- Lord Cornwallis
- None of the above

GOVERNANCE FOR INDIAN ASM
- 1995: full fledged Department for Indian Systems of Medicine & Homeopathy was created under MoHFW
– To promote and regulate Indian ASM
- 2002: National Policy on Indian Systems of Medicine & Homeopathy
- 2003: Dept. renamed as Department of AYUSH
– Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy
- 2014: fully independent Ministry of AYUSH
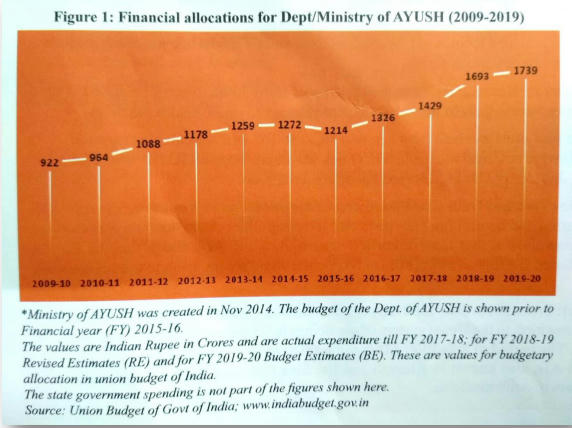
FINANCIAL ALLOCATION TO AYUSH
ASM IN NUMBERS
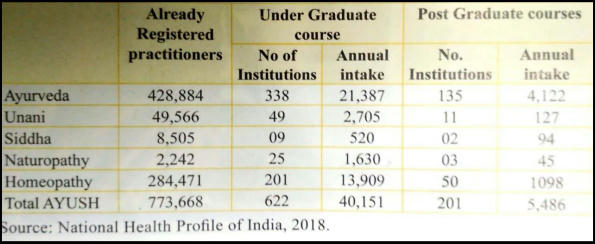
- Current utilization of AYUSH services ranges from 5- 10% of total health service utilization via about 4k hospitals and 28k dispensaries
WAY FORWARD
- Functional linkage of AYUSH at all levels of health systems, including service delivery as well as workforce
- Inclusion of Yoga at workplace, in schools and community in light of increasing NCDs
- Building knowledge base and integrating scientific evidence in ASM is necessary to check on quacks
























 WhatsApp
WhatsApp