Table of Contents


ABOUT THE INTERNAL WORKING GROUP
- An internal working group led by M K Jain was formed by RBI in February 2019.
- It submitted its report in September 2019.
- Its mandate was to provide recommendations on agricultural credit, especially the impact of farm loan waivers on state finances.
- The working group was to study 3 aspects:-
- Factors that drive agricultural credit
- Building a cost-effective and inclusive credit system
- Enforcing credit discipline (impact of loan waivers on state finances and agricultural credit).
BACKGROUND
- Right at the time of RBI’s inception in 1935, it was felt that the central bank should pay special attention to agri credit.
- So, the RBI Act laid foundation to a special Agricultural Credit Department to study the problems and coordinate with the agencies concerned.
- Department was rechristened as the Rural Planning & Credit Department.
- Till date, there have been several committees and working groups to study and suggest measures to boost agri credit.
FINDINGS OF THE REPORT
- The ratio of agri credit outstanding to agri GDP increased from 0.6% in 1950-51 to 10% in 1971-72 and 22% by 1987-88.
- It was due to several policies such as 5-year plans, bank nationalisation, the bank branch policy and priority sector lending.
- But the ratio declined during 1991 economic reforms, which led to the start of Kisan Credit Card scheme in 1998.
- This coupled with other measures paid off as the ratio zoomed to the 50% level as of today.
- Institutional source of agri credit with a mere 10% share in 1951, now reads 72%.
- So the main objectives of the committee is to suggest ways to increase the percentage of institutional finance.
RECOMMENDATIONS OF THE GROUP
- Digitise land records and make them accessible to banks for easier verification of collateral.
- Make a federal institution on the lines of the GST Council to take inputs from both the Centre and states.
- Banks should leverage technology in a major way and explore collaborations with agri-tech companies.
- For small and medium farms (SMFs), banks should not insist on land records for loans up to Rs 2 lakh.
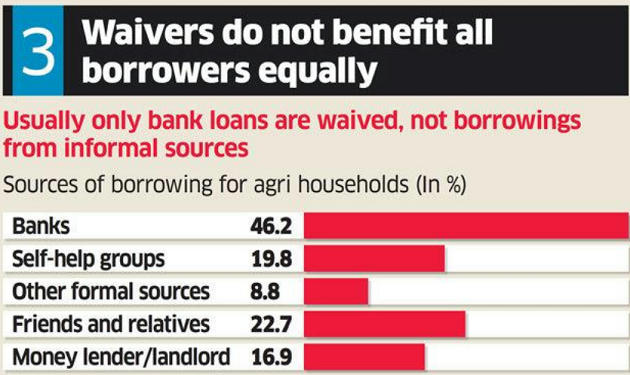
- The committee also noted that there is a wide disparity across states when it comes to agri credit.
- The ratio of agri credit to state GDP is highest at 200% for Kerala and just 20% for the North-East and West Bengal.
OTHER RECOMMENDATIONS
- Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF) should be used as a tool to deepen credit absorption in these states.
- The RIDF, set up under NABARD in 1995, gets funds from commercial banks to make up for shortfall in priority sector loan targets.
- The report asked state governments to conduct awareness initiatives for land consolidation to achieve economies of scale.
- The working group favours DBT compared to interest subvention schemes.
- It proposed that the governments avoid waiver and instead make the existing policies more efficient.
- The Indian agriculture system is a maze with several ministries and organisations responsible for different tasks.
- Thus, any committee recommendations are often lost in the process.
- To avoid this, the Jain committee has marked out specific ministries and organisations against each suggestion, which is really helpful.


Latest Burning Issues | Free PDF





















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp