Table of Contents
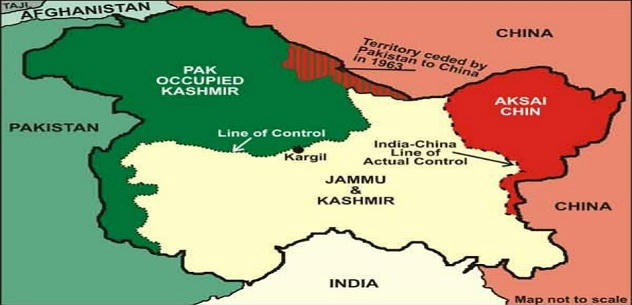
KASHMIR
ARTICLE 370
- Article 370 of the Indian constitution is an article that gives autonomous status to the state of Jammu and Kashmir.
- The article is drafted in Part XXI of the Constitution: Temporary, Transitional and Special Provisions.
- The Constituent Assembly of Jammu and Kashmir, after its establishment, was empowered to recommend the articles of the Indian constitution that should be applied to the state or to abrogate the Article 370 altogether.
ARTICLE 370
- The state of Jammu and Kashmir’s original accession, like all other princely states, was on three matters: defence, foreign affairs and communications.
- All the princely states were invited to send representatives to India’s Constituent Assembly, which was formulating a constitution for the whole of India. They were also encouraged to set up constituent assemblies for their own states.
- The rulers and chief ministers of all the states met and agreed that separate constitutions for the states were not necessary. They accepted the Constitution of India as their own constitution
AARTICLE 370
- In the case of Jammu and Kashmir, the representatives to the Constituent Assembly requested that only those provisions of the Indian Constitution that corresponded to the original Instrument of Accession should be applied to the State.
- The Article has become a permanent feature of the Indian constitution, as confirmed by various rulings of the Supreme Court of India and the High Court of Jammu and Kashmir, the latest of which was in April 2018 PROVISIONS
- It exempted the State from the complete applicability of the Constitution of India. The State was allowed to have its own Constitution.
- Central legislative powers over the State were limited, at the time of framing, to the three subjects of defence, foreign affairs and communications.
- Other constitutional powers of the Central Government could be extended to the State only with the concurrence of the State Government.
- The ‘concurrence’ was only provisional. It had to be ratified by the State’s Constituent Assembly.
- The State Government’s authority to give ‘concurrence’ lasted only until the State Constituent Assembly was convened. Once the State Constituent Assembly finalised the scheme of powers and dispersed, no further extension of powers was possible. • The Article 370 could be abrogated or amended only upon the recommendation of the State’s Constituent Assembly.
JAMMU AND KASHMIR
- Preamble and Article 3 of the Constitution of Jammu and Kashmir states that the State of Jammu and Kashmir is and shall be an integral part of the Union of India.
- Article 5 states that the executive and legislative power of the State extend to all matters except those with respect to which Parliament has power to make laws for the State under the provisions of the Constitution of India.
- The constitution was adopted on 17 November 1956 and came into force on 26 January 1957
























 WhatsApp
WhatsApp