Table of Contents
MCQ 1
Fedor, recently in news was a
- Spacecraft
- Moon Lander
- Spacerobot
- None
MCQ 2
Cryodrakon boreas is a
- Recently found amphibian
- An invasive plant species
- The largest flying bird of all time
- None
MCQ 3
- Market Intervention Price Scheme is to protect the growers of these horticultural/agricultural commodities from making distress sale in the event of bumper crop
- Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices ia the implementing agency
Choose correct
(A) Only 1
(B) Only 2
(C) Both
(D) None
- The government is planning to procure almost 12 lakh metric tonnes of apple this season, under the MISP.
About the Market Intervention Price Scheme:
- It is a price support mechanism implemented on the request of State Governments.
- It is for procurement of perishable and horticultural commodities in the event of a fall in market prices.
- The Scheme is implemented when there is at least 10% increase in production or 10% decrease in the ruling rates over the previous normal year.
- Its objective is to protect the growers of these horticultural/agricultural commodities from making distress sale in the event of bumper crop during the peak arrival period when prices fall to very low level.
- The Department of Agriculture & Cooperation is implementing the scheme.

Funding:
- Under MIP, funds are not allocated to the States.
- Instead, central share of losses as per the guidelines of MIP is released to the State Governments/UTs, for which MIP has been approved, based on specific proposals received from them.
- The area of operation is restricted to the concerned state only.
- The MIS has been implemented in case of commodities like apples, kinnoo/malta, garlic, oranges, galgal, grapes, mushrooms, clove, black pepper, pineapple, ginger, red-chillies, coriander seed etc.
- Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) is a decentralized agency of the Government of India. It was established in 1965 as the Agricultural Prices Commission, and was given its present name in 1985.
- It is an attached office of the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Government of India.
MCQ 4
AITIGA goods agreement is between India &
- Nepal
- Myanmar
- EU
- ASEAN
- India and the 10-member ASEAN have agreed to initiate a review of the bilateral free trade agreement (FTA) in goods to make it more user-friendly, simple and trade facilitative.
- The countries have also agreed to initiate the review of the ASEANIndia trade in goods agreement to make it more user-friendly, simple, and trade facilitative for businesses.
About AITIGA
- The ASEAN–India Free Trade Area (AIFTA) is a free trade area among the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and India.
- It came into force from January 2010.
- Under the pact, two trading partners set timelines for eliminating duties on the maximum number of goods traded between the two regions.
- Based on preliminary ASEAN data, two-way goods trade with India grew by 9.8 per cent from $73.6 billion in 2017 to $80.8 billion in 2018.
Need for review
- India is not happy about the fact that its trade deficit with ASEAN has widened significantly since the pact was implemented.
- A NITI Aayog study reveals that India’s trade deficit with ASEAN doubled to $10 billion in 2017 from $5 billion in 2011.
- One of the reasons for the growing deficit is the low utilisation of the FTA route by Indian exporters to ASEAN countries because of difficulties faced in negotiating the rules.
- A review of the India-ASEAN FTA could help improve utilisation in India by making the pact simpler and more user-friendly.
MCQ 5
- Fall Armyworm is a dangerous bloodsucking worm for humans
- It was first found in Karnataka and its endemic to India
Choose correct
(A) Only 1
(B) Only 2
(C) Both
(D) None
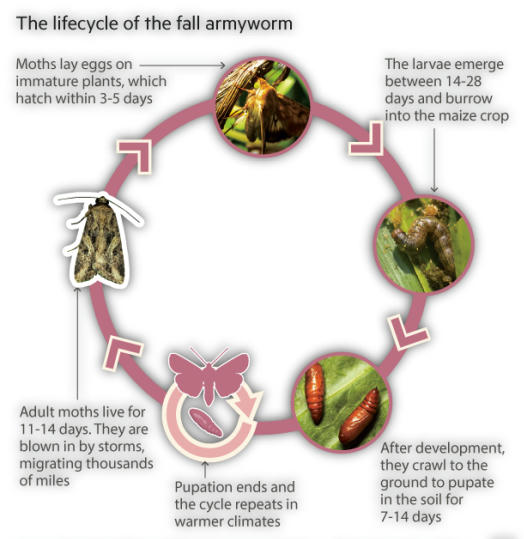
- Maize crops falling victim to fall armyworm in Bihar. Reports of the pest attacking crops have been reported from a number of districts in the state, India’s third-largest maize producer.
- It is a native of the tropical and sub-tropical regions of the Americas
- First detected in the African continent in 2016. Since then, it has spread to other countries such as China, Thailand, Malaysia and Sri Lanka.
- In India: It was reported in India for the first-time in Karnataka. Within a span of only six months, almost 50 per cent of the country, including Mizoram, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and West Bengal, has reported FAW infestations.
- It is the polyphagous(ability to feed on different kinds of food) nature of the caterpillar and the ability of the adult moth to fly more than 100 km per night.
- Given its ability to feed on multiple crops — nearly 80 different crops ranging from maize to sugarcane — FAW can attack multiple crops.
- Similarly, it can spread across large tracts of land as it can fly over large distances. This explains the quick spread of the pest across India.
- Till date, India has reported FAW infestation on maize, sorghum (jowar) and sugarcane crops.
- Maize has been the worst affected as most maize-growing states in southern India have been affected by the pest.
- FAW infestation and drought has led to a shortfall of nearly 5 lakh tonnes in output, prompting the central government to allow import of maize under concessional duty. Maize is the third most important cereal crop grown in the country and the infestation, if not checked in time, can wreck havoc.
MCQ 6
- Sardar Sarovar Dam is the biggest dam in terms of volume of concrete used in it.
- It is funded by ADB
Choose correct
(A) Only 1
(B) Only 2
(C) Both
(D) None
- The Sardar Sarovar Dam is a gravity dam on the Narmada river near Navagam, Gujarat in India. Four Indian states, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharastra and Rajasthan, receive water and electricity supplied from the dam. The foundation stone of the project was laid out by Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru on 5 April 1961.
- The project took form in 1979 as part of a development scheme funded by the World Bank through their International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, to increase irrigation and produce hydroelectricity, using a loan of US$ 200 million.
- The construction for dam begun in 1987, but the project was stalled by the Supreme Court of India in 1995 in the backdrop of Narmada Bachao Andolan over concerns of displacement of people.
- In 2000-01 the project was revived but with a lower height of 110.64 metres under directions from SC, which was later increased in 2006 to 121.92 meters and 138.98 meters in 2017
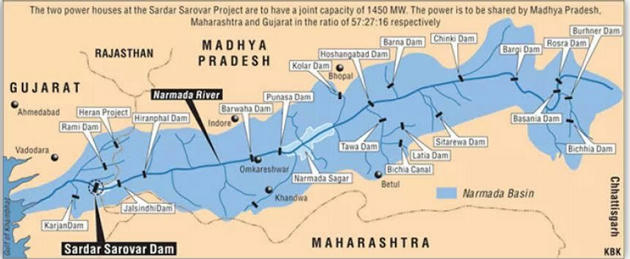
Sardar Sarovar project- key facts
- Taken up after the Narmada Water Disputes Tribunal gave its final award vis-à-vis Gujarat-Madhya Pradesh in 1979.
- Second biggest dam in terms of volume of concrete used in it.
- Third highest concrete dam in India.
- Power generated from the dam would be shared among three states — Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Gujarat. What’s the concern with the project?
- Water level in the submergence area of the dam in Barwani and Dhar districts of Madhya Pradesh is rising steadily.
- As per Narmada Bachao Andolan group, 40,000 families in 192 villages in Madhya Pradesh would be displaced when the reservoir is filled to its optimum capacity.
- According to the World Bank, the project started with very little assessment of resettlement and rehabilitation, and environmental impact.
MCQ 7
- Droughts affect 42 per cent of India’s land while another 6 per cent is ‘exceptionally dry plane
- Drought Preparedness report released in ongoing CoP14 has suggested a national drought management policy commission
Choose correct
(A) Only 1
(B) Only 2
(C) Both
(D) None
- Framework for the Assessment of Benefits of Action/Cost of Inaction for Drought Preparedness report has been released at the ongoing 14th Conference of Parties (COP14) to the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD).
- Droughts affect 42 per cent of India’s land while another 6 per cent is ‘exceptionally dry plane’.
- 40 per cent of the country’s population is vulnerable to droughts The
10-point framework
- Appoint a national drought management policy commission
- State or define the goals and objectives of risk-based national drought management policy
- Seek stakeholder participation, define and resolve conflicts between key water use sectors
- Inventory data and financial resources available and broadly identify groups at risk
- Prepare the key tenets of the national drought management policy and preparedness plans
- Identify research needs and fill institutional gaps
- Integrate science and policy aspects of drought management
- Publicize the policy and preparedness plans, build public awareness
- Develop education programs for all age and stakeholder groups
- Evaluate and revise policy and supporting plans
MCQ 8
1995 Basel Ban Amendment was regarding
- Banking standards
- Species conservation
- Trade of endangered plants
- hazardous wastes
- The 1995 basel ban amendment, a global waste dumping prohibition, has become an international law after croatia (97th country to ratify) ratified it on september 6, 2019.
- It will become a new article in the convention and will enter into force in the 97 countries after 90 days — on december 5.
- Adopted by the parties to the Basel Convention in 1995.
- To protect human health and the environment against the adverse effects of hazardous wastes.
- The amendment prohibits all export of hazardous wastes, including electronic wastes and obsolete ships from 29 wealthiest countries of the Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) to non-OECD countries.
- Basel Convention — Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal:
- Opened for signature on 22 March 1989
- entered into force on 5 May 1992
- Parties — 187.
- It is an international treaty that was designed to reduce the movements of hazardous waste between nations, and specifically to prevent transfer of hazardous waste from developed to less developed countries (LDCs).
- It does not address the movement of radioactive waste.
Download Free PDF





















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp