Table of Contents
Food Chain and Food Web
- The flow of energy from producer to top consumers is called energy flow which is unidirectional.
- To understand the energy flow through the ecosystem we need to study about the trophic levels [tropical level interaction].
- Trophic level is the representation of energy flow in an ecosystem. The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food chain.
- Trophic level interaction deals with how the members of an ecosystem are connected based on nutritional needs.
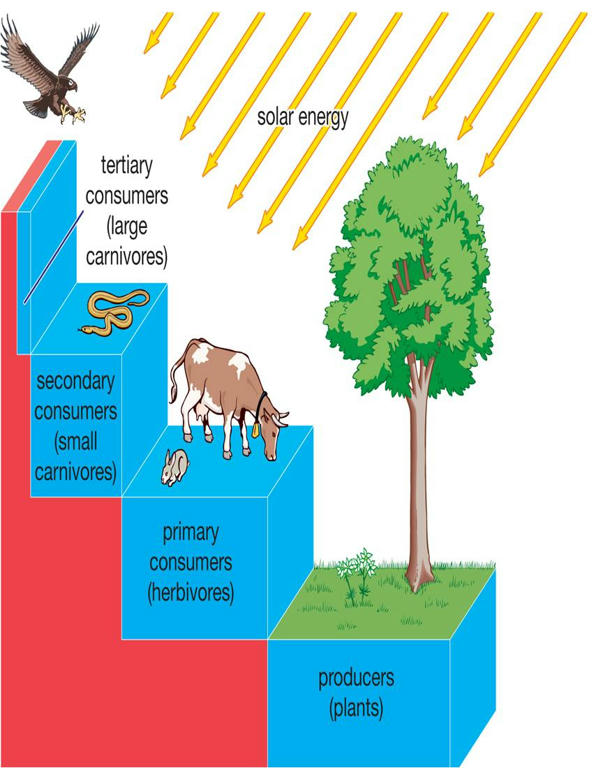
- Energy flow is a fundamental process and happens in all ecosystems. Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. The movement of energy through a series of organisms in an ecosystem is what is called energy flow in an ecosystem.
- Organisms are either producers or consumers in terms of the energy flow through the ecosystem. Plants are producers. They take energy from sunlight and convert it into organic material through the process of photosynthesis.
Food Chain
- A food chain may be defined as the transfer of energy and nutrients through a succession of organisms through repeated process of eating and being eaten.
Food Web
- In nature, there are several food chains. These food chains are not independent of each other but interlinked to one another. An organism on one food chain can be eaten by several other creatures. Also, bigger carnivores need not always consume a carnivore one step lesser in the food chain. They may directly consume herbivores. This leads to complex food webs and not linear chains.


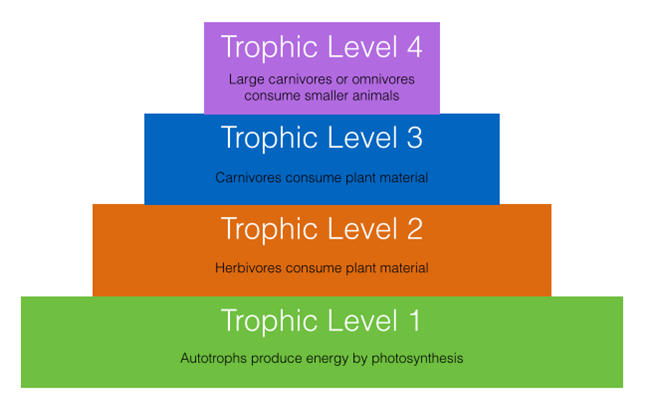
- Trophic levels
- Autotrophs Green plants (Producers)
- Heterotrophs Herbivore (Primary consumers)
- Heterotrophs Carnivores (Secondary consumers)
- Heterotrophs Carnivore (Tertiary consumers)
- Heterotrophs Top carnivores (Quaternary consumers)

Food Chain
- Transfer of food energy from green plants (producers) through a series of organisms with repeated eating and being eaten link is called a food chain. E.g. Grasses → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk/Eagle.
- Grazing food chain
- Detritus food chain
- Grazing food chain
- The consumers which start the food chain, utilising the plant or plant part as their food, constitute the grazing food chain.
- Detritus food chain: It starts from dead organic matter of decaying animals and plant bodies consumed by the micro-organisms and then to detritus feeding organism called detrivores or decomposer and to other predators.

Food Web
- Multiple interlinked food chains make a food web.
- Food web represents all the possible paths of energy flow in an ecosystem.
- If any of the intermediate food chains is removed, the succeeding links of the chain will be affected largely.
- The food web provides more than one alternative for food to most of the organisms in an ecosystem and therefore increases their chance of survival.
Biotic Interaction
- The interaction that occurs among different individuals of the same species is called intraspecific interaction while the interaction among individuals of different species in a community is termed as interspecific interaction
Mutualism
- This is a close association between two species in which both the species benefit. For example the sea anemone, a cnidarian gets attached to the shell of hermit crabs for benefit of transport and obtaining new food while the anemone provides camouflage and protection by means of its stinging cells to the hermit crab.
Neutralism
- Neutralism describes the relationship between two species which do interact but do not affect each other. y True neutralism is extremely unlikely and impossible to prove
Amensalism
- One species harms or restricts the other species without itself being adversely affected or harmed by the presence of the other species. y Organisms that secrete antibiotics and the species that get inhibited by the antibiotics are examples of amensalism.
Predation
- Predators like leopards, tigers and cheetahs use speed, teeth and claws to hunt and kill their prey. y They keep prey populations under control. But for predators, prey species could achieve very high population densities and cause ecosystem instability.
Parasitism
- In this type of interaction, one species is harmed and the other benefits. Parasitism involves parasite usually a small size organism living in or on another living species called the host from which the parasite gets its nourishment and often shelter.
Competition
- This is an interaction between two populations in which both species are harmed to some extent. Competition occurs when two populations or species, both need a vital resource that is in short supply
Commensalism
- In this relationship one of the species benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited. y Some species obtain the benefit of shelter or transport from another species. For example sucker fish, remora often attaches to a shark by means of its sucker which is present on the top side of its head. This helps the remora get protection, a free ride as well as meal from the left over of the shark’s meal. The shark does not however get any benefit nor is it adversely affected by this association.
Q) With reference to the food chains in the ecosystem, which of the following kinds of organisms is/are known as decomposer/decomposers? (2013)
- Virus
- Fungi
- Bacteria
Select the correct answer using the code below
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q) With reference to the food chains in the ecosystem, which of the following kinds of organisms is/are known as decomposer/decomposers? (2013)
- Virus
- Fungi
- Bacteria
Select the correct answer using the code below
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.)With reference to food chains in ecosystems, consider the following statements:
- A food chain illustrates the order in which a chain of organisms feed upon each other.
- Food chains are found within the populations of a species.
- A food chain illustrates the numbers of each organism which are eaten by others.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- None
Q.)With reference to food chains in ecosystems, consider the following statements:
- A food chain illustrates the order in which a chain of organisms feed upon each other.
- Food chains are found within the populations of a species.
- A food chain illustrates the numbers of each organism which are eaten by others.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- None
Latest Burning Issues | Free PDF






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp