- SakhiMatdan Kendras Are Set Up In Each Assembly Segment In
- Uttarakhand
- UP
- Haryana
- Karnataka
MCQ 2
- Shangri-La dialogue is related to
- Asian cultural identity
- Security forum
- Asia’s best rated hotel
- Bussinessmeet
- The IISS Asia Security Summit: The Shangri-La Dialogue (SLD) is a “Track One” inter-governmental security forum held annually by an independent think tank, the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) which is attended by defense ministers, permanent heads of ministries and military chiefs of 28 Asia-Pacific states. The forum gets its name from the Shangri-La Hotel in Singapore where it has been held since 2002.
MCQ 3
- Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission is announced by
- ISRO
- JAXA
- ESA
- NASA
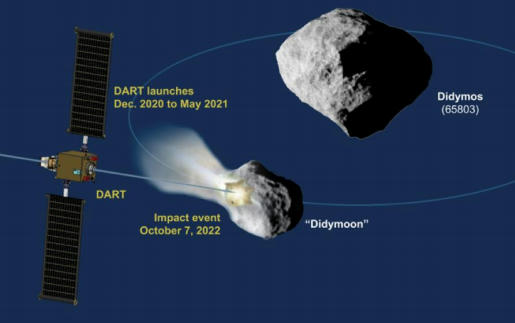
- Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) is a planned space probe that will demonstrate the kinetic effects of crashing an impactor spacecraft into an asteroid moon for planetary defense purposes. The mission is intended to test whether a spacecraft impact could successfully deflect an asteroid on a collision course with Earth.
- A demonstration of an asteroid deflection is a key test that NASA and other agencies wish to perform before the actual need of planetary protection is present. DART is a joint project between NASA and the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), and it is being developed under the auspices of NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office.
- In August 2018, NASA approved the project to start the final design and assembly phase.
- In Live Address Delivered 400 Feet Underwater, Seychelles President Calls on Humanity to Protect the Oceans
MCQ 4
- Choose correct regarding 4th Resilient Cities Asia-Pacific (RCAP) Congress
- It was launched in 2015 after paris summit with the goal of forging partnerships and dialogues that matter.
- Congress 2019 was recently organized by the International Council for Local Environmental Initiatives (ICLEI) in association with South Delhi Municipal Corporation.
(A) Only 1
(B)Only 2
(C) Both
(D)None
- About Resilient Cities Asia-Pacific:
- It is the annual global platform for urban resilience and climate change adaptation.
- It is convened by ICLEI – Local Governments for Sustainability and co-hosted by the World Mayors Council on Climate Change and the City of Bonn.
- It was launched in 2010 with the goal of forging partnerships and dialogues that matter.
- The Asia-Pacific Forum on Urban Resilience and Adaptation – Resilient Cities Asia Pacific Congress (RCAP) is a response to heightened demand from the Asia Pacific Region, which encouraged ICLEI to expand the congress series to include Resilient Cities Asia-Pacific, bringing the event and the focus to the Asia-Pacific region, catering to the situation, challenges and opportunities of local governments specifically in this region.
- Aim: To provide an Asian platform for urban resilience and climate change adaptation where partnerships are forged and concrete dialogues are happening, with the ultimate goal of identifying solutions and creating lasting impacts for cities in the region.
MCQ 5
- Nirbhay Missile has an operational range of 300 km and can carry warheads of up to 1000 kg including nuclear warheads.
- Its speed is more than speed of sound
- Choose correct
(A)Only 1
(B)Only 2
(C)Both
(D)None
- The Election Commission of India is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for administering election processes in India.
- The body administers elections to the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha and state Legislative Assemblies and Legislative Council in India, and the offices of the President and Vice President in the country.
- The Election Commission operates under the authority of Constitution per Article 324, and subsequently enacted Representation of the People Act.
- The commission has the powers under the Constitution, to act in an appropriate manner when the enacted laws make insufficient provisions to deal with a given situation in the conduct of an election. Being a constitutional authority, Election Commission is amongst the few institutions which function with both autonomy and freedom, along with the country’s higher judiciary, the Union Public Service Commission and the Comptroller and Auditor General of India.
- The current commission was established in 1950 when it had a Chief Election Commissioner appointed. Membership increased on 16 October 1989 to three with the increase of two Commissioners were appointed to the commission. That commission ceased on 1 January 1990 when The Election Commissioner Amendment Act, 1989 superceded the earlier the commission; it continues in operation.. Decisions by the commission are by at least a majority vote. The Chief Election Commissioner and the two Election Commissioners who are usually retired IAS officers draw salaries and allowances as per with those of the Judges of the Supreme Court of India as per the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners (Conditions of Service) Rules, 1992
- The commission secretariat is based in New Delhi which includes the Election Commissioners, Deputy Election Commissioners (usually IAS officers) Directors General, Principal Secretaries, Secretaries and Under Secretaries.
- Administration is generally by state with the Chief Electoral Officer of the State, who is an IAS officer of Principal Secretary rank. At the district and constituency levels, the District Magistrates (in their capacity as District Election Officers), Electoral Registration Officers and Returning Officers perform election work
- Removal from office
- The Chief Election Commissioner of India can be removed from office as can be a judge of the Supreme Court of India: a two-thirds majority resolution passed by the Parliament of India (Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha) outlining the grounds of misbehavior or incapacity. Other Election Commissioners can be removed by the President of India on the advice of the Chief Election Commissioner. A Chief Election Commissioner has yet to be impeached. In 2009, just before the 2009 Lok Sabha Elections, Chief Election Commissioner N. Gopalaswami sent a recommendation to President Prathibha Patil to remove Election Commissioner Navin Chawla, who was soon to take office as the chief election commissioner and to subsequently supervise the Lok Sabha Election, a potential conflict of interest considering his partisan political party behavior.The President rejected advisory recommendation. Subsequently, after Gopalswami’s retirement the next month, Chawla became the chief election commissioner and supervised the 2009 Lok Sabha Elections
- By the “Election Commission (Condition Of Service Of Election Commissions And Transaction Of Business) Act, 1991”, the salary of the chief election commissioner is the same as salary of a Judge of Supreme Court of India.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp