Table of Contents

- Code on Industrial Relations is one of the 4 proposed labour bills long envisaged to replace 44 archaic labour laws.
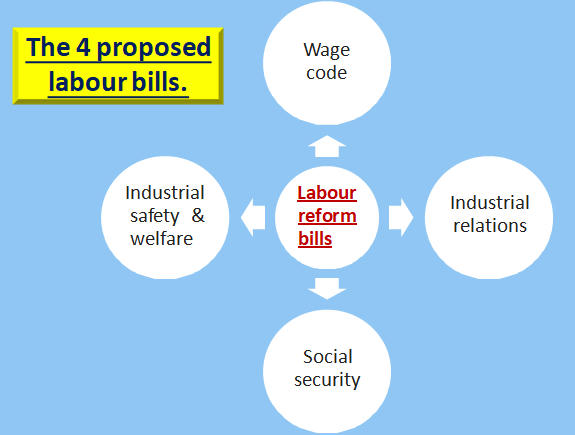
- The industrial relations code is the third out of four labour codes that have got approval from the cabinet.
- The Labour Code on Wages has already been approved by Parliament in August.
- While the Labour Code on Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions has been referred to the standing committee of labour.
- This code is meant to simplify and merge three central labour acts including:-
- The Trade Unions Act, 1926,
- The Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1946, The Industrial Disputes Act, 1947.
MAIN IDEA BEHIND THE NEW CODE
- The idea is to improve the working conditions of the contractual staff and bring them on par with the regular employees.
HOW WILL IT BENEFIT EMPLOYERS?
- Since the idea is to improve working conditions of the contractual staff and bring them on par with the regular employees,
- Thus a company need not have multiple employment policies for contractual and regular staff.
- Especially for areas like maternity leave and extended leave for mothers, a similar policy will be followed which would make the management process easier.
- In the past, leaves were a bone of contention between companies and labourers.
- A crucial aspect of the new draft code is the fixed-term employment proposal that has also been welcomed by the industry.
- This will mean that the respective companies would not need to engage with any third-party contractors.
- Instead, under the new regime, they will be able to hire contract workers directly for a fixed tenure.
- Based on the type of job role, the contract period can be tweaked making it easier for firms to hire and fire.
- Earlier, the contractors would play a role in these matters.
- Now, the employment period can be decided by the company itself.
- Later, if the particular job gets redundant, worker can let go.
- For instance, if a welding professional has been hired, and the company is able to procure a machine to perform the same function at a later date, this professional can be laid off.
- In the past, firing staff would lead to a dispute since there was no concept of a fixed-term employment.
HOW WILL IT HELP EMPLOYEES?

- At present, labour disputes take a long time to be resolved.
- The Industrial Relations Code has proposed setting up of a two-member tribunal for settling labour disputes.
- Earlier, there was a one-member team that led to delays in getting a resolution.

- Further, a few government officers would also be given the power to look into cases and also impose penalties.
- This is expected to ease the burden on the tribunals that are already handling several thousand cases.
- This will ease the pain for employees who otherwise lose pay while attending the often- prolonged tribunal hearings.
- The social security benefits will be extended to all types of workers.
- This means that all company benefits including insurance and leave encashment could be provided to these workers.
- Earlier, contractors would be passed on these benefits, and there were reports of leakage of cash/insurance amount.
CONCERNS
- For workers, being relevant from a skilling perspective has been a cause of concern in India.
- Re-skilling of staff will be a key priority under the new regulations.
- The government has said that there will be re-skilling fund that will be utilised for crediting to workers.
- There is also the fear of retrenchment.
- While there was fear of only mid-sized companies (with 300 or more employees) being mandated to take government permission to retrench staff,
- The draft code has retained it for companies with 100 employees or above.
- This means even if a small company/factory were to take a retrenchment decision, they would have to get prior permission from the government to do so.
CHALLENGE FROM STATES
- The biggest challenge will be in getting these labour codes approved in the near term and persuading states, to come on board,
- As it is under the concurrent list.
WHAT THE ECONOMIC SURVEY SAYS?
- This year’s Economic Survey made the point that- Units in states that have made the transition towards more flexible labour markets were 25.4% more productive than their counterparts.

WHY THEY ARE VERY IMPORTANT FOR A COUNTRY LIKE INDIA?
- In an economy where 10 million young people enter the labour market annually, there is indeed a strong case for greater flexibility on these laws.
- Even more so considering that Vietnam, Indonesia and Bangladesh are far more competitive in labour intensive sector and taking advantage of US-China trade war.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp