Table of Contents
What is a Non-Banking Financial Company?
- NBFCs are financial institutions that offer various banking services but do not have a banking license.
- These institutions are not allowed to take traditional demand deposits.
- In India, NBFC is a company registered under theCompanies Act, 1956 engaged in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of shares/stocks/bonds/debentures/securities, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance business, chit business etc.
What has happened?
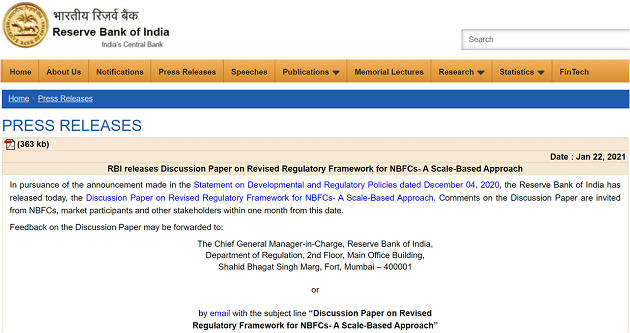
- Reserve Bank of India on Friday released discussion paper on revised regulatory framework for Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs).
- Regulatory framework for NBFCs needs to be re-oriented to keep pace with changing realities in financial sector, the central bank said.
Why this new framework?
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has proposed a tighter regulatory framework for non-banking financial companies,
- By creating a four-tier structure with a progressive increase in intensity of regulation.
- RBI has said the regulatory and supervisory framework of NBFCs should be based on a four-layered structure:
- Base Layer, Middle Layer, Upper Layer and a Top Layer.
- It has also proposed classification of non-performing assets (NPAs) of base layer NBFCs from 180 days to 90 days
- NBFCs in lower layer will be known as NBFC-Base Layer m(NBFC-BL).
- NBFCs in middle layer will be known as NBFC-Middle Layer (NBFC-ML).
- An NBFC in the Upper Layer will be known as NBFC-Upper Layer (NBFC-UL) and will invite a new regulatory superstructure.
So, what?
- Once an NBFC is identified as NBFC-UL, it will be subject to enhanced regulatory requirement at least for four years from its last appearance in the category,
- Even where it does not meet the parametric criteria in the subsequent year.
- “Hence, if an identified NBFC-UL does not meet the criteria for classification for four consecutive years, it will move out of the enhanced regulatory framework,” it said.
- The NBFC sector has seen tremendous growth in recent years.
- In last five years alone, size of balance sheet of NBFCs (including HFCs) has more than doubled from Rs 20.72 lakh crore (2015) to Rs 49.22 lakh crore (2020).
The 4 layers
- BASE LAYER: If the framework is visualised as a pyramid, the bottom of the pyramid, where least regulatory intervention is warranted.
- It can consist of NBFCs, currently classified as non-systemically important NBFCs (NBFC-ND), NBFCP2P lending platforms, Type I NBFCs etc.
- MIDDLE LAYER: As one moves up, the next layer can consist of NBFCs currently classified as systemically important NBFCs (NBFC-ND-SI), deposit taking NBFCs (NBFC-D), housing finance companies, IFCs, IDFs, SPDs and core investment companies.
- The regulatory regime for this layer will be stricter compared to the base layer.
- Adverse regulatory arbitrage vis-à-vis banks can be addressed for NBFCs falling in this layer in order to reduce systemic risk spill-overs, where required, the RBI said.
- UPPER LAYER: Going further, the next layer can consist of NBFCs which are identified as systemically significant
- This layer will be populated by NBFCs which have large potential of systemic spill-over of risks and have the ability to impact financial stability.
- There is no parallel for this layer at present, as this will be a new layer for regulation.
- The regulatory framework for NBFCs falling in this layer will be bank-like, albeit with suitable and appropriate modifications, it said.
- TOP LAYER: It is possible that considered supervisory judgment might push some NBFCs from out of the upper layer of the systemically significant NBFCs for higher regulation/supervision.
- These NBFCs will occupy the top of the upper layer as a distinct set.
- Ideally, this top layer of the pyramid will remain empty unless supervisors take a view on specific
- In other words, if certain NBFCs lying in the upper layer are seen to pose extreme risks as per supervisory judgement, they can be put to higher and bespoke regulatory/supervisory requirements.
Conclusion
- In view of the recent stress in the sector, it has become imperative to re-examine the suitability of this regulatory approach,
- Especially when failure of an extremely large NBFC can precipitate systemic risks, the RBI paper said.
- The regulatory framework for NBFCs needs to be reoriented to keep pace with changing realities in the financial sector.
Q) Which of the following statements regarding NBFCs in India?
- Top 50 NBFC accounts for 80% of market share by loans.
- In last 10 years the compounded annual growth rate of NBFCs have been more than commercial banks.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 & 2
- None of the above
Latest Burning Issues | Free PDF
























 WhatsApp
WhatsApp