Table of Contents
WHY IN NEWS
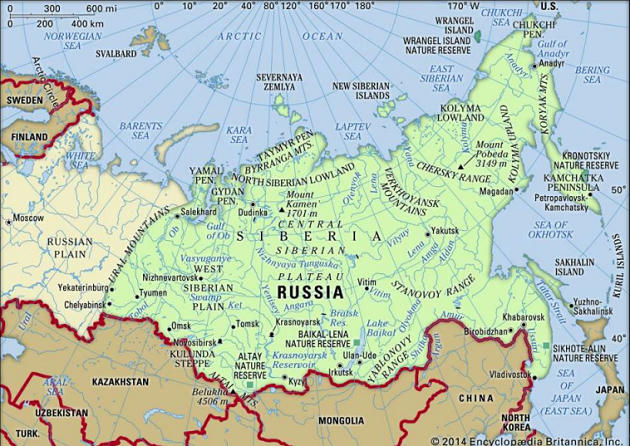
- President Vladimir Putin of Russia has declared a state of emergency in northern Siberia after a huge oil spill in the river Ambarnaya.
- More than 20,000 tons of diesel leaked into the Ambarnaya River near the city of Norilsk last Friday, after a fuel tank collapsed at a power plant.
- Oil spill turned the river Ambarnaya crimson and threatened to inflict significant damage to the Arctic environment.
WHY IN NEWS
- THE EFFECTS OF OIL SPILLS
- Environmental effects
- Social effects
- Economic effects
ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS
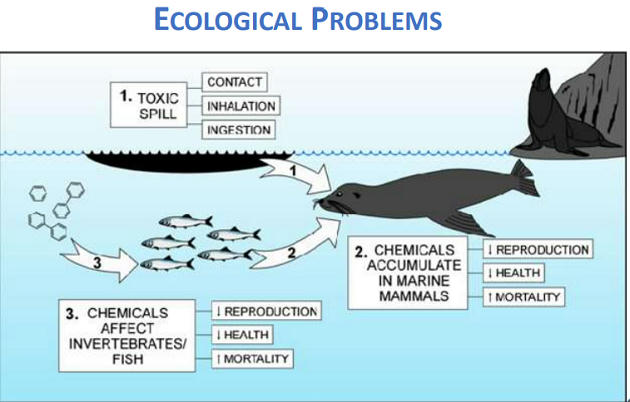
- Water pollution is a direct result of an oil spill. The chemical composition of oil mixes with the water and creates a new substance known as “mousse.“
- This mousse becomes even more sticky than oil alone, causing it to stick to organisms.
- Mousse resembles food for a number of animals and also attracts certain curious birds and marine life. Which results into either death or bioaccumulation of oil.

ECOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
- Animals can suffer detrimental effects on their fur and feathers. For example, a seal pup’s fur will break down, causing it to experience hypothermia.
- This same effect is responsible for the majority of bird deaths in oil slicks.

ECOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
- Outright ingestion of oil creates toxins in the system. This is seen in animals in the immediate vicinity of the oil spill and also by animals farther up the food chain.
- One long-term effect on animals is the fact that most birds and reptiles exposed to an oil slick have the side effect of producing thinner egg shells.
- Algae and sea grass becomes tainted. This can make the entire ecosystem uninhabitable for years.
SOCIAL EFFECTS
- Oil spills effects social life of humans in long term. With destroyed ecosystem , the coastal people are forced to rely on government assistance to continue their lives in the area.
- With all manner of sea life destroyed, the culture could not continue to flourish and became essentially a welfare community with a very poor economy.
ECONOMIC EFFECTS
- The overall cost and challenge of cleaning up an oil spill is enormous. The spill could cost hundreds of billions of dollars in cleaning the oil spill, environmental compensations and possible loss of revenue from spill area.

CLEANING UP OIL SPILLS
- Using Oil Booms The use of oil booms is a very simple and popular method of controlling oil spills. Equipment called containment booms acts like a fence to prevent the oil from further spreading or floating away.

CLEANING UP OIL SPILLS
- Using Skimmers Once the oil has been confined by using oil booms, skimmers or oil scoops can be deployed onto boats to remove the contaminants from the water surface. Skimmers are machines specially designed to suck up the oil from the water surface like a vacuum cleaner

CLEANING UP OIL SPILLS
- Using Sorbents Sorbents are materials that soak up liquids by either absorption (pulling in through pores) or adsorption (forming a layer on the surface). Both these properties make the process of clean-up much easier. Materials commonly used as oil sorbents are hay, peat moss, straw or vermiculite.

CLEANING UP OIL SPILLS
- Burning In-situ In this method, the oil floating on the surface is ignited to burn it off. This in-situ burning of oil can effectively remove up to 98% of an oil spill, which is more than most of the other methods.

CLEANING UP OIL SPILLS
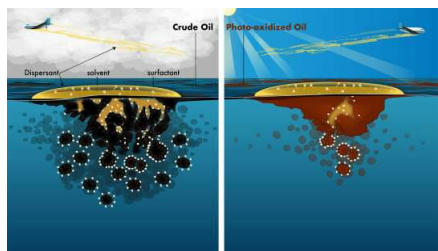
- Using Dispersants When the spilled oil cannot be contained by using booms, the only option left is to accelerate the disintegration of oil. Dispersal agents, such as Corexit 9500, are chemicals that are sprayed upon the spill with the help of aircraft and boats, which aid the natural breakdown of oil components
CLEANING UP OIL SPILLS
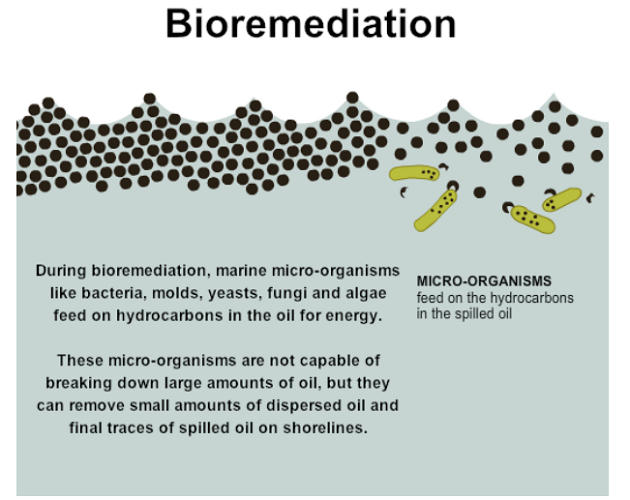
- Bioremediation Bioremediation refers to the use of specific microorganisms to remove any toxic or harmful substances. There are various classes of bacteria, fungi, archaea and algae that degrade petroleum products by metabolizing and breaking them into simpler and non-toxic molecules (mostly fatty acids and carbon dioxide)
HOW OIL SPILL OCCURRED IN RUSSIA
- The power plant at Nornickel company in Norilsk is built on permafrost soil.
- Temperature rise caused by climate change weakened the permafrost soil.
- This caused the pillars that supported the plant’s fuel tank to sink.
- Around 20,000 tonnes of diesel oil was released into the Ambarnaya river, which has since drifted 12 km on its surface.


Latest Burning Issues | Free PDF























 WhatsApp
WhatsApp