Table of Contents
SATELLITE INTERNET
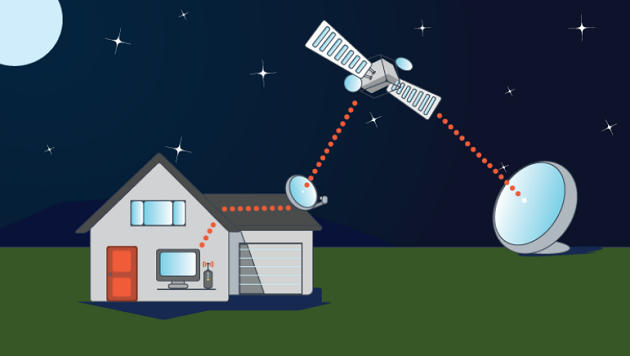
- Satellite Internet access is Internet access provided through communications satellites
- Companies providing home internet service include ViaSat, through its Exede brand, and EchoStar, through subsidiary HughesNet.
COMPANIES
- Companies providing home internet service include ViaSat, through its Exede brand, and EchoStar, through subsidiary HughesNet.
- OneWeb, a new startup that aims to send thousands of satellites into orbit, in hopes of delivering fiber-optic-fast internet to the remotest parts of the world.
USED IN INDIA AS WELL

STARLINK BY ELON MUSK

STARLINK
- Starlink is a satellite constellation development project underway by American company SpaceX to develop a low-cost, high-performance satellite bus and requisite customer ground transceivers to implement a new spacebased Internet communication system.
Starlink

STARLINK PLANS
- SpaceX has deployed 62 satellites as of May 2019 and plans to deploy 60 more per launch, at a rate of one launch every two weeks beginning November 2019.
- In total, nearly 12,000 satellites will be deployed and later possibly up to 42,000 satellites.
THE PLANS
- Total cost of Starlink will be around 60 billion dollars
- As detailed in a 2016 revenue projection obtained by The Wall Street Journal, SpaceX estimated that by 2025 its launch services would be pulling down approximately $5 billion in revenue, which was dwarfed by the projected $30 billion for its Starlink internet services. The company hasn’t released any details about the price structure for its internet service or how much ground stations for users will cost.

STARLINK

DOES STARLINK POSE A SPACE DEBRIS THREAT?
- We’re talking about a constellation that — if it ever comes to full fruition — would include up to 12,000 members. Several nations have launched almost 9,000 satellites over the past six decades.
- Of these, about 5,000 are still in orbit. So we are talking about doubling the amount of traffic in space over a couple of years, or over a decade at most, compared to the last 60 years.
DEBRIS PROBLEM
- There are no binding rules currently in place for how long a satellite can safely linger in orbit. The United Nations recommends that satellites be deorbited no more than 25 years after the end of their missions, but these guidelines lack strict penalties for noncompliance.





















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp