Table of Contents
- Contents
- Introduction
- Tax Proposals
- Urban Landscape
- Transport Infrastructure
- Industries
- Financial Sector
- Water & Sanitation
- Universal Health Coverage
- Education
- Skills, Employment & HRD
- Agriculture
- Environment & Forest
- Gender Budgeting & Elderly
- Northeast Development
Introduction
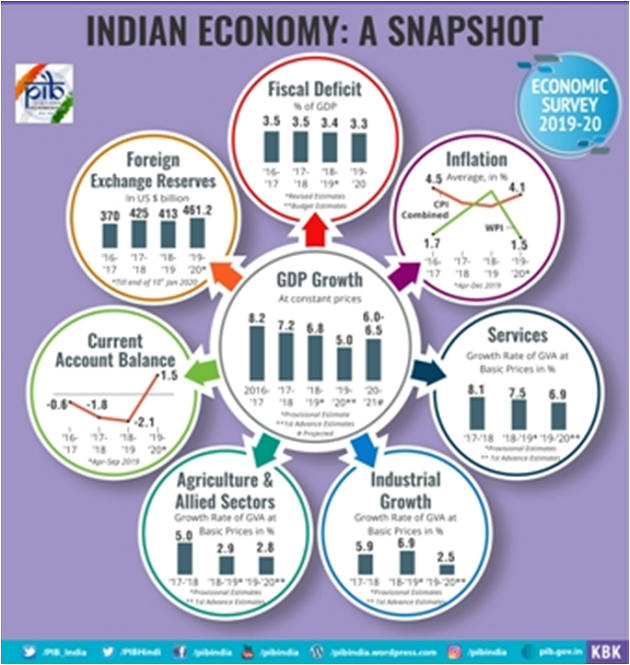
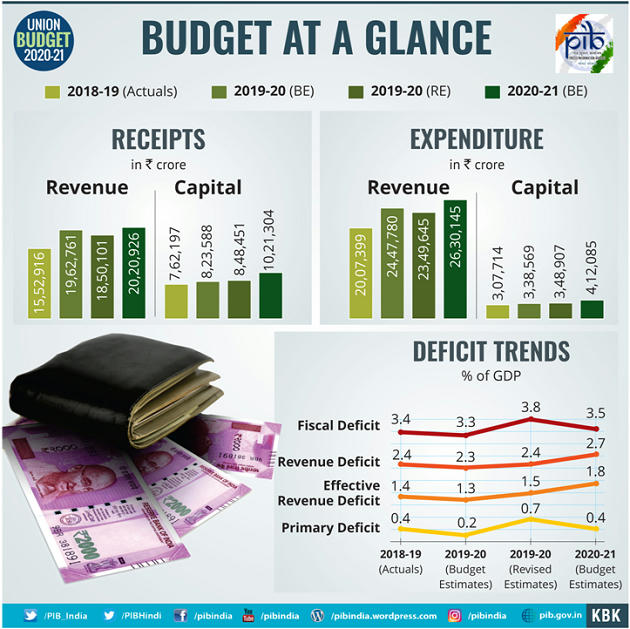
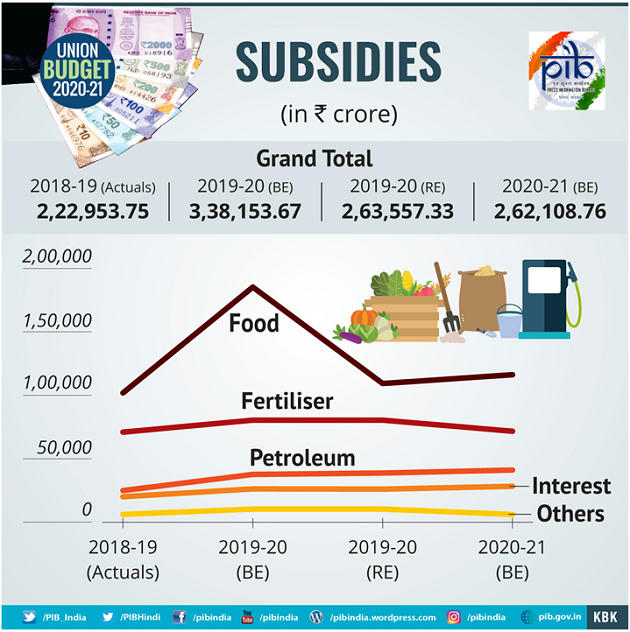
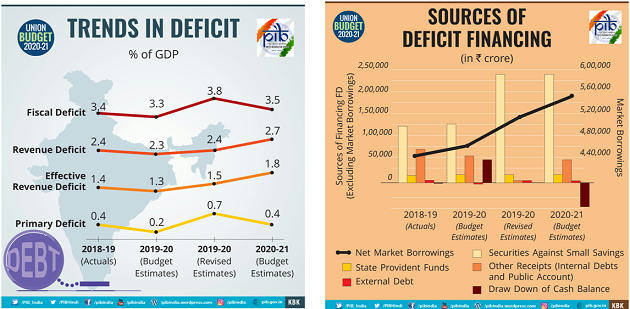
Tax Proposals
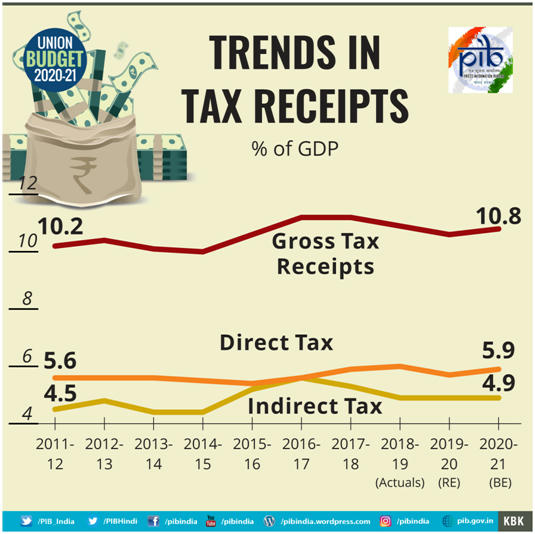
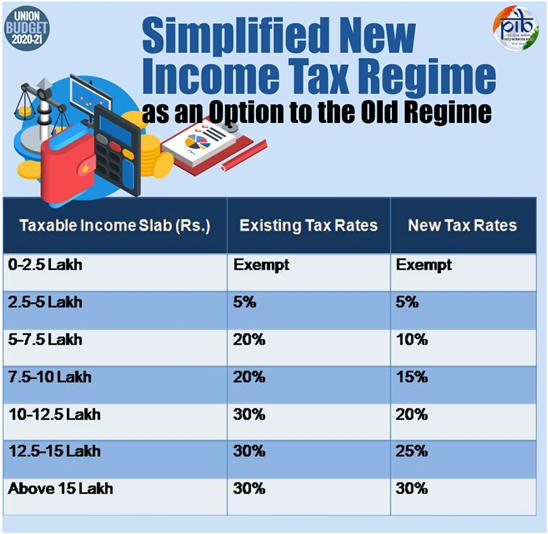
Others | Direct Tax
- Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) removedmaking India a more attractive investment destination
- Start-ups with turnover up to Rs. 100 crore to enjoy 100% deduction for 3 consecutive assessment years out of 10 years.
- Tax payment on ESOPs deferred
- Cooperative societies exempted from Alternate Minimum Tax (AMT) just like Companies are exempted from the Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT).
- Tax concession for foreign investments:
- 100% tax exemption to the interest, dividend and capital gains income on investment made in infrastructure and priority sectors before 31stMarch, 2024 with a minimum lock-in period of 3 years by the Sovereign Wealth Fund of foreign governments.
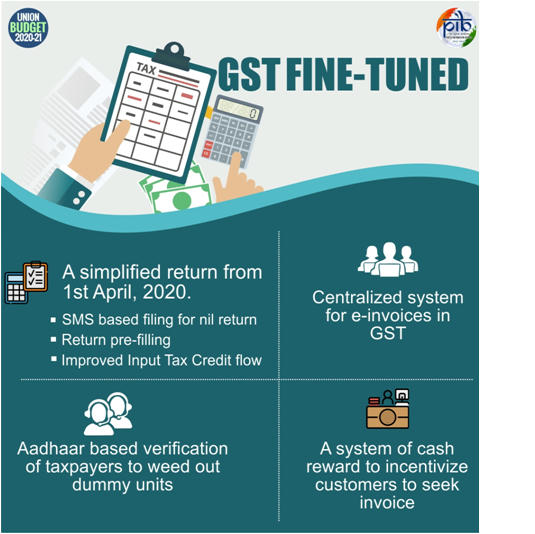
Others | Indirect Tax
- Excise duty proposed to be raised on Cigarettes and other tobacco products, no change made in the duty rates of bidis.
- Customs Act being amended to enable proper checks of imports under FTAs.
- Anti-dumping duty on PTA abolished to benefit the textile sector.
- Provisions for checking dumping of goods and imports of subsidized goods being strengthened.
- Q #1
- Vivad Se Vishwas’ scheme is aimed at reducing litigations in:
- direct taxes
- indirect taxes
- Both 1 & 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
3. Urban Landscape
- Story in numbers
- Urban Population
- Currently – 34%
- By 2030 – 40%
- By 2050 – 50%
- Urban share of GDP
- 2009-10 – 62-63%
- 2030 – 75%
Urbanization Strategy of India
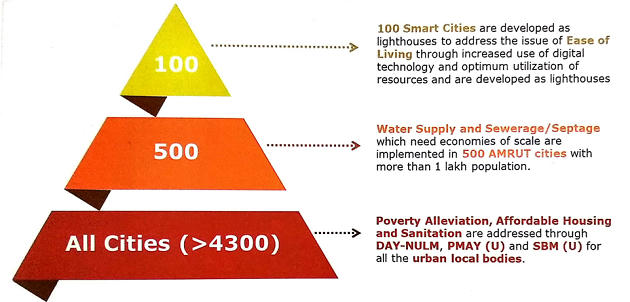
- Overall Investment in Urban Rejuvenation
Progress | SBM
- B/w 2014 & 2020
- 10 Cr toilets in rural areas
- 65 L household toilets + 6 L public toilets in urban areas
- 60% municipal wards practice source segregation (from 41%)
- All cities of 35 States/UTs => ODF
- 699 districts, 2.5 L GPs and 6 L villages => ODF

AMRUT
- Focuses on ensuring:
- water supply, sewerage and septage management
- storm water drainage
- urban transport
- availability of green and open spaces
- reform management and support
- capacity building

Progress |AMRUT
Key figures:
- More than 5000 projects under construction/completion
- 64% urban households have tap water supply
- On track to achieve 62% sewerage coverage by 2020
Key reforms:
- Online Building Permission System in more than 1500 ULBs
- Replacement of streetlights with LED lights (74 Lakh)
- Credit Rating (36 cities have A and higher rating)
- Municipal Bonds worth Rs. 3300 Cr issued
- Ahmedabad, Amravati, Bhopal, Hyderabad, Pune, Surat & Vizag
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan – Urban (July 2019) – for water conservation
Progress | SCM
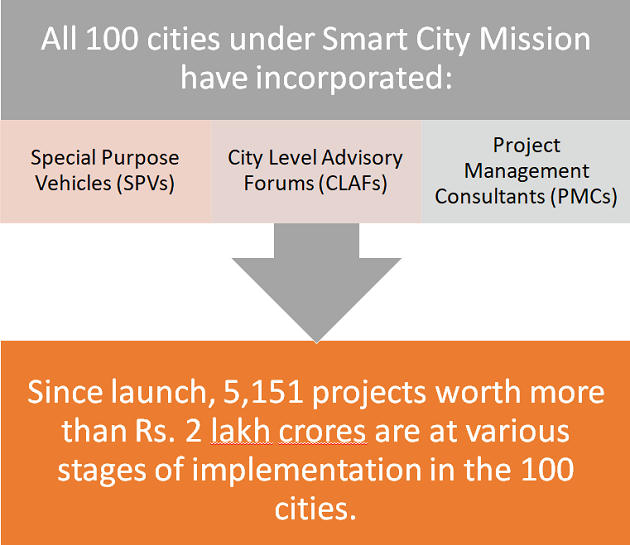
Progress | SCM

PMAY (U)
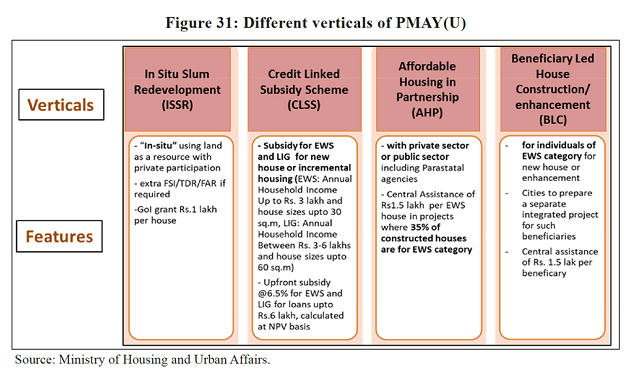
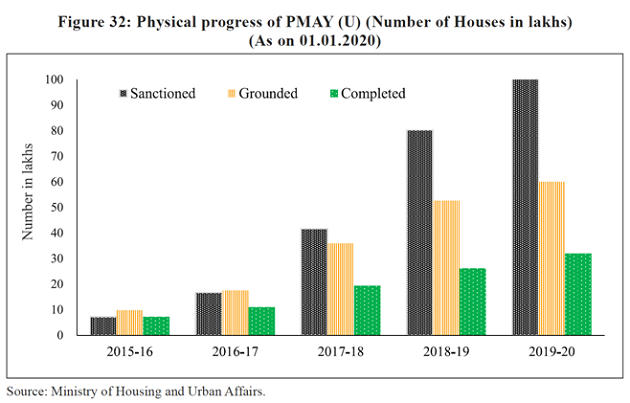
Progress | PMAY (U)
- It is rapidly moving towards achieving the vision for providing a pucca house to every household by 2022.
- Out of 1.03 crore houses approved, 60 lakhs have been grounded for construction, of which 32 lakh houses have been completed and delivered.
Progress | EODB
- Budget announcements
- National Infrastructure Pipeline
- 103 lakh crore worth projects; launched on 31st December 2019 for the period 2020-2025.
- More than 6500 projects across sectors, to be classified as per their size and stage of development.
- 16% has been earmarked for urban rejuvenation
- 1-year internships to fresh engineers in all ULBs in order to enhance the skill of the youth
4. Transport Infra
Context
- To achieve the GDP of $5 trillion by 2024-25, India needs to spend about $1.4 trillion (` 100 lakh crore) over these years on infrastructure
Roads
- Road transport is the dominant mode of transportation in terms of its contribution to Gross Value Added (GVA) and traffic share.
- As per Govt. report, in 2011-12, road transport is estimated to handle 69% and 90% of the countrywide freight and passenger traffic
- As on Mar 2018, India had a road network of about 59.64 lakh km. The total length of NHs was 1.32 lakh km as on Mar 2019.
- The pace at which roads have been constructed has grown from 17 kms per day in 2015-16 to 29.7 kms per day in 2018-19.
- However, the pace seems to have moderated to 12 kms per day in 2019-20.

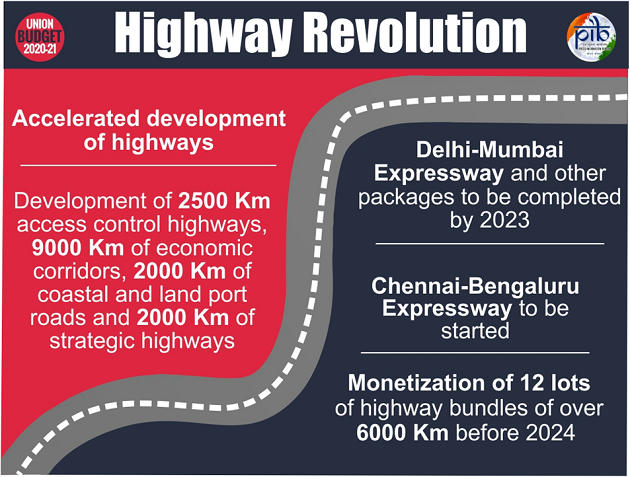
Railways
- Indian Railways (IR) with over 68,000 route kms is the third largest network in the world under single management.
- During 2018-19, it carried 120 crore tonnes of freight and 840 crore passengers making it the world’s largest passenger carrier and 4th largest freight carrier.
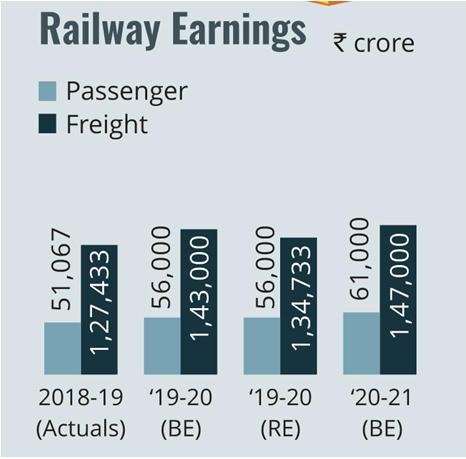
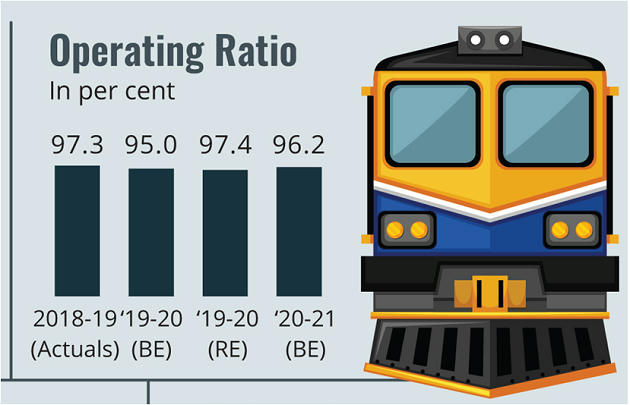

Critical Challenges in Railways Modernization
- Fundamentals of how PPPs would be encouraged
- R&D for indigenous manufacturing of Rolling Stock
Aviation
- India is the 3rd largest domestic market for civil aviation in the world.
- India has 136 commercially-managed airports by AAI and 6 under PPP for Operation, Maintenance and Development of airports.
- A total of 43 airports have been operationalized under UDAN
- To ease the strain, 100 more airports are to be made operational by FY 2023-24
- To bring in efficiency and resources, 6 airports (Ahmedabad, Guwahati, Jaipur, Lucknow, Mangalore, and Thiruvananthapuram) have been taken up for development under PPP mode
Focus areas in Aviation
- Increasing capacity and service levels in top 30 airports via PPP
- Increasing no. of airports to about 100 and ensuring that all tier II and tier III cities have their own airports
- Attracting PPPs in lower tier cities is difficult because of viability – may need VGF / subsidies to make workable
- AAI is fallback option but concerns about AAI managing many loss-making airports is there
Shipping
- Around 95% of India’s trade by volume and 68% in terms of value is transported by sea.
- Despite one of the largest merchant shipping fleet (> 1400) among developing countries, India’s share in total world dead weight tonnage (DWT) is only 0.9% as on January 1, 2019 according to Institute of Shipping Economics and Logistics.
Issues highlighted by Professor G Raghuram
- Sagarmala is not proceeding at the pace envisaged – a part of the problem is environment but there is also a problem of need
- Capacity additions may not be needed unless for captive purposes
- There could possibly be a situation of excess capacity in container domain
- Could also be the case for coal – as power sector moves towards renewables
- Some earlier PPPs not able to perform well due to restrictive concession agreements
- Need restructuring of regulatory regime
- Connectivity issues on land side, esp. rail, should improve with DFCs and formation of Indian Port Rail Corp. Ltd. (formed in 2015)

Air & Rail for Farm
- Krishi Udaanto be launched by the Ministry of Civil Aviation:
- Both international and national routes to be covered.
- North-East and tribal districts to realize Improved value of agri-products
- Kisan Railto be setup by Indian Railways through PPP:
- To build a seamless national cold supply chain for perishables (milk, meat, fish, etc.
- Express and Freight trains to have refrigerated coaches.
Money?…….National Infrastructure Pipeline
- Launched on 31 Dec 2019, would commence in phases from 2020-21 to 2024-25
- 103 lakh crore worth projects
- Energy = 24%
- Urban = 16%
- Roads = 19% | Railways = 13% | Airports = 1.3% | Ports = 1%
- More than 6500 projects across sectors, to be classified as per their size and stage of development.
- Central Govt. (39%) and State Govt. (39%) will have equal share in funding followed by Private Sector (22%).
- It is expected that private sector share may increase to 30% by 2025.
- Q #2
- Vivad Se Vishwas’ scheme is aimed at reducing litigations in:
- direct taxes
- indirect taxes
- Both 1 & 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
5. Industries
Industry, Commerce & Investment
- Investment Clearance Cellproposed to be set up:
- To provide “end to end” facilitation and support
- To work through a portal
- National Technical Textiles Missionto be set up:
- With four-year implementation period from 2020-21 to 2023-24.
- At an estimated outlay of Rs 1480 crore.
- To position India as a global leader in Technical Textiles.
- New scheme NIRVIKto achieve higher export credit disbursement

Industry, Commerce & Investment
- Turnover of Government e-Marketplace (GeM) proposed to be taken to Rs 3 lakh crore.
- Scheme for Revision of duties and taxes on exported products to be launched.
- Exporters to be digitally refunded duties and taxes levied at the Central, State and local levels, which are otherwise not exempted or refunded.
- All Ministries to issue quality standard orders as per PM’s vision of “Zero Defect-Zero Effect” manufacturing.
Infrastructure
- 100 lakh crore to be invested on infrastructure over the next 5 years
- National Logistics Policy to be released soon:
- To clarify roles of the Union Government, State Governments and key regulators.
- A single window e-logistics market to be created
- Focus to be on generation of employment, skills and making MSMEs competitive.
- National Skill Development Agency to give special thrust to infrastructure-focused skill development opportunities.
- Project preparation facility for infrastructure projects proposed.
- To actively involve young engineers, management graduates and economists from Universities.
- infrastructure agencies to involve youth-power in start-ups.
Infrastructure | Connectivity
- To take advantage of new technologies:
- Policy to enable private sector to build Data Centre parks throughout the country to be brought out soon
- Fibre to the Home (FTTH) connections through Bharatnet to link 100,000 GPs this year
- 6000 crore proposed for Bharatnet programme in 2020-21
Startups
- A digital platform to be promoted to facilitate seamless application and capture of IPRs.
- Knowledge Translation Clusters to be set up across different technology sectors including new and emerging areas.
- Mapping of India’s genetic landscape- Two new national level Science Schemes to be initiated to create a comprehensive database.
- Early life funding proposed, including a seed fund to support ideation and development of early stage Start-ups.

Financial Sector

- Q #3
- Vivad Se Vishwas’ scheme is aimed at reducing litigations in:
- direct taxes
- indirect taxes
- Both 1 & 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
7. Water & Sanitation



Protocols
- ODF protocol – independent third party certifies a city as ODF on satisfying certain requirements. To prevent it from slippage, the certification has to be renewed every 6 months.
- ODF+ protocol – to track maintenance of acceptable levels of cleanliness in community/public toilets so that they are functional and actually used by citizens. 739 cities are ODF+.
- ODF++ protocol – to track what was happening to faecal sludge being discharged from the toilets => for complete sewage and faecal sludge management. 292 cities are ODF++.
- SBM Water+ focuses on ensuring that no untreated wastewater is discharged into the open environment.
8. Universal Health Coverage
- Q #4
- Vivad Se Vishwas’ scheme is aimed at reducing litigations in:
- direct taxes
- indirect taxes
- Both 1 & 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
9. Education
10. Skills, Employment & HRD
- Q #5
- Vivad Se Vishwas’ scheme is aimed at reducing litigations in:
- direct taxes
- indirect taxes
- Both 1 & 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
11. Agriculture
12. Environment & Forest
Q #6
- Vivad Se Vishwas’ scheme is aimed at reducing litigations in:
- direct taxes
- indirect taxes
- Both 1 & 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
13. Gender Budgeting & Elderly
14. NE Development
- Q #7
- Vivad Se Vishwas’ scheme is aimed at reducing litigations in:
- direct taxes
- indirect taxes
- Both 1 & 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Download Free PDF – Yojana Magazine






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp